Figure 4.
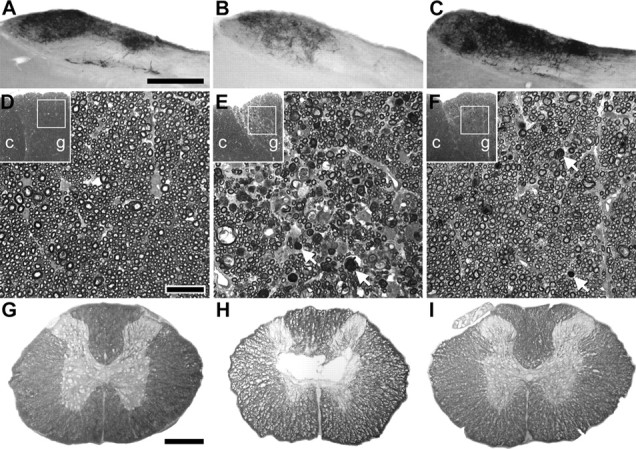
PTP inhibition provides lasting protection of dorsal column sensory axons and white matter after a spinal cord contusion. The rats infused for 28 d starting 4 h after contusion (Fig. 3) were analyzed 2 weeks later. A, B, Compared with sham-operated rats (A), injured ones infused with PBS (B) showed a reduction in CTB-traced innervation from the hindlimb to the gracile nucleus. C, bpV(phen)-infused rats had an apparently normal innervation (compare also with Fig. 1B). Scale bar, 500 μm. D, E, The number of myelinated axons in the fasciculus gracilis (g) at C3 was reduced in PBS-infused rats (E) compared with sham rats (D). Arrows, Examples of myelin debris. F, The bpV(phen)-treated rats had an apparently normal number of axons. c, Fasciculus cuneatus. Scale bar, 20 μm. G–I, Injury-induced loss of white matter at the injury epicenter (H, PBS-infused rat) was reduced after infusion of bpV(phen) (I) to sham levels (G). Scale bar, 500 μm.
