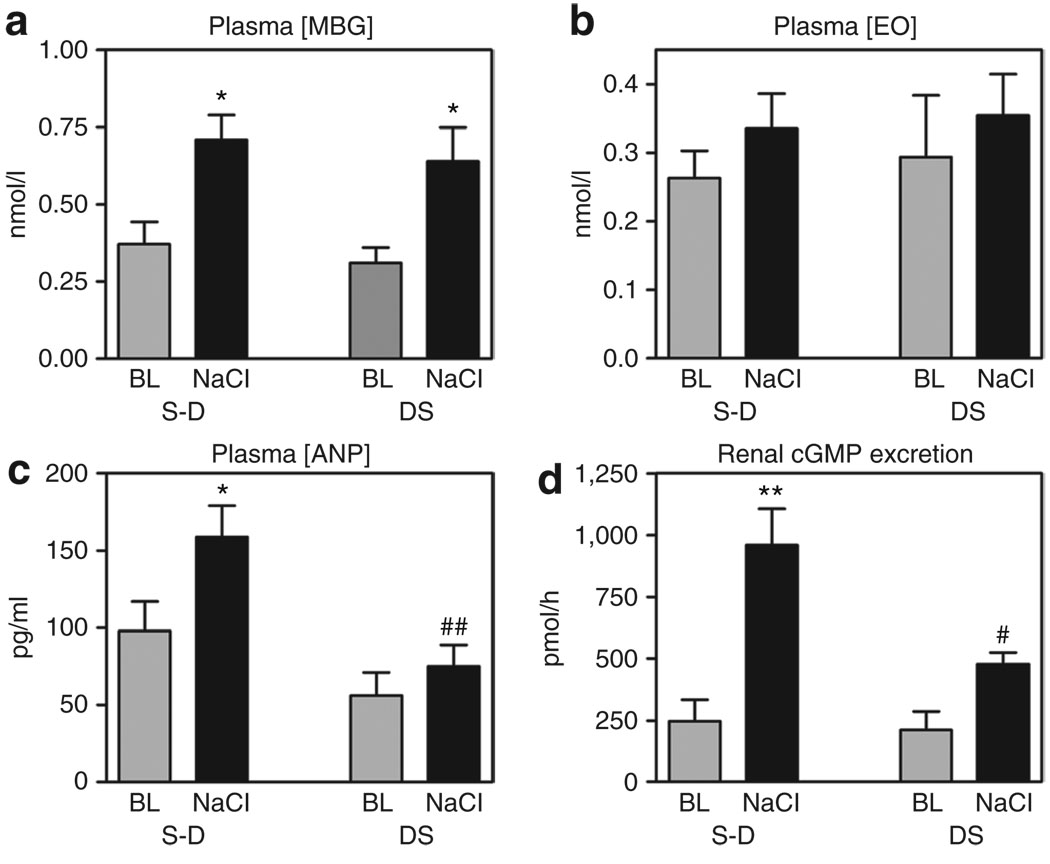
Figure 2.
Effect of NaCl loading on plasma levels of marinobufagenin (MBG), endogenous ouabin (EO), atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), and on renal excretion of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Plasma levels of (a) MBG, (b) EO, (c) ANP, and (d) renal excretion of cGMP in Sprague-Dawley (S-D) and Dahl salt-sensitive rats (DS) following intraperitoneal administration of hypertonic solution of NaCl, and at baseline (BL). Each bar represents means ± s.e.m. from 10 observations. By one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Newman–Keuls test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 vs. BL; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. NaCl-loaded S-D. Source of variations by two-way ANOVA: plasma MBG (NaCl effect: P = 0.002; strain effect: P = 0.43), plasma EO (NaCl effect: P = 0.29; strain effect: P = 0.69), plasma ANP (NaCl effect: P = 0.038; strain effect: P = 0.002), renal cGMP excretion (NaCl effect: P < 0.0001; strain effect: P = 0.026).