Abstract
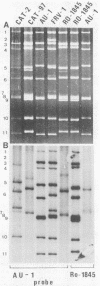
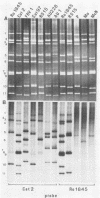
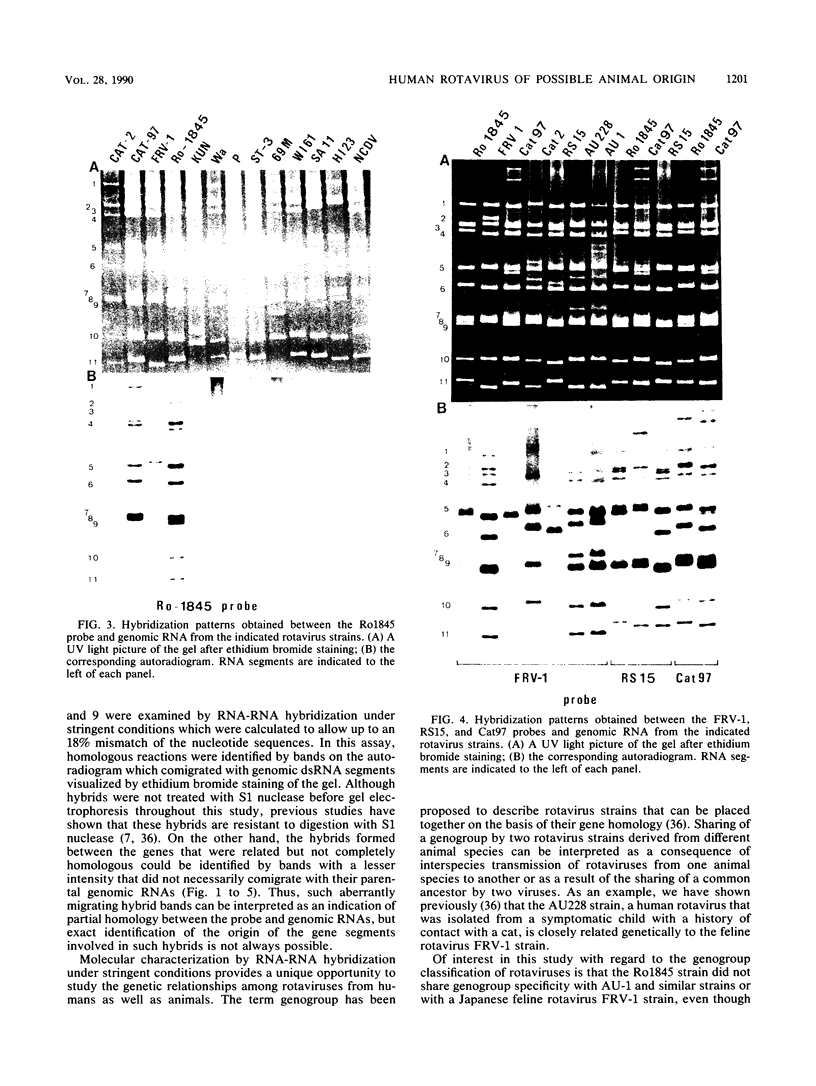
With a few exceptions subgroup I group A human rotavirus strains have short RNA patterns, whereas most animal rotavirus strains belong to subgroup I and have long RNA patterns. Thus, new isolates of subgroup I human rotaviruses with long RNA patterns are considered to have a high likelihood of being animal rotaviruses. A group of human rotaviruses represented by the AU-1 strain has recently been shown to be genetically related to a feline rotavirus (FRV-1) isolated in Japan. A human rotavirus, strain Ro1845, which is similar to the AU-1 strain in its subgroup (I), serotype (3), and electropherotype (long), was compared with various human and animal strains by RNA-RNA hybridization to determine its genogroup, a term proposed to classify rotaviruses based on their gene homology. The Ro1845 strain did not show a significant level of homology with AU-1, FRV-1, or other human strains, indicating that the Ro1845 strain is different in its genogroup not only from the AU-1 strain but also from other human strains. However, the Ro1845 strain showed a high degree of homology with another feline rotavirus (Cat97) isolated previously in Australia, suggesting that the Ro1845 strain might originate from a feline rotavirus that is genetically distinct from the Japanese FRV-1 strain. Furthermore, the Ro1845 strain as well as the Cat97 strain were related genetically to the canine rotavirus RS15 strain. Taken together, these results indicate that at least two genogroups are present in feline rotaviruses, one resembling the AU-1 strain and the other resembling the Ro1845 strain as well as canine rotaviruses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboudy Y., Shif I., Zilberstein I., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Use of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies and analysis of viral RNA in the detection of unusual group A human rotaviruses. J Med Virol. 1988 Jul;25(3):351–359. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch C. J., Heath R. L., Marshall J. A., Liu S., Gust I. D. Isolation of feline rotaviruses and their relationship to human and simian isolates by electropherotype and serotype. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2731–2735. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Mathan M. M., Mathew M., Martin R., Beards G. M., Mathan V. I. Rotavirus epidemiology in Vellore, south India: group, subgroup, serotype, and electrophoretype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2410–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2410-2414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Dimitrov D. H. The molecular epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1984;29:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Hoshino Y., Boeggeman E., Purcell R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among animal rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1986;87(3-4):273–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01315305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. In vitro transcription of two human rotaviruses. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1032-1037.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Boeggeman E., White L., Perez M., Purcell R., Hoshino Y., Midthun K., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez I., White L., Perez M., Kalica A. R., Marquina R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses as determined by RNA hybridization. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):648–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.648-655.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Naik T. N. Detection of a large number of subgroup 1 human rotaviruses with a "long" RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1989;105(1-2):119–127. doi: 10.1007/BF01311122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the major neutralization protein of four human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. Gene coding assignments for growth restriction, neutralization and subgroup specificities of the W and DS-1 strains of human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Baldwin C. A., Scott F. W. Isolation and characterization of feline rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):313–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Scott F. W., Appel M. J. Isolation and characterization of a canine rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1982;72(1-2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01314456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Wada R., Hirasawa K., Akiyama Y., Oda T. Isolation of equine rotavirus in cell cultures from foals with diarrhea. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Feb;46(1):1–9. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaoka S., Nakagomi T., Fukuhara N., Hoshino Y., Suzuki H., Nakagomi O., Kapikian A. Z., Ebina T., Konno T., Ishida N. Serologic characteristics of a human rotavirus isolate, AU-1, which has a "long" RNA pattern and subgroup I specificity. J Med Virol. 1987 Dec;23(4):351–357. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuzawa T., Konno T., Suzuki H., Ebina T., Ishida N. Two distinct electrophoretic migration patterns of RNA segments of human rotaviruses prevalent in Japan in relation to their serotypes. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(3):271–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Nakagomi O. Antigenic and molecular characterization of bovine rotaviruses isolated in Japan. Res Virol. 1989 Jul-Aug;140(4):337–350. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(89)80114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Kono M., Underdahl N. R., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can Vet J. 1971 Mar;12(3):69–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki M., Sameshima R., Ata M., Minami K., Okabayashi K., Harasawa R. Characterization of canine rotavirus RS 15 strain and comparison with other rotaviruses. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Aug;47(4):531–538. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki M., Yamakawa M. Detection of rotaviruses in cat feces. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1987 Feb;49(1):159–160. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.49.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N. Identification of rotavirus genogroups by RNA-RNA hybridization. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Sep;3(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Oyamada H., Suto T. Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in Japanese children with acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1985 Sep;17(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N., Katsushima N., Nakagomi O. Occurrence of changes in human rotavirus serotypes with concurrent changes in genomic RNA electropherotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2586–2592. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2586-2592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Katsushima N., Nakagomi O. Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups I and II in relation to "short" and "long" electrophoretypes of viral RNA. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1988 Jul-Sep;139(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2617(88)80043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Matsuda Y., Ohshima A., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi O. Characterization of a canine rotavirus strain by neutralization and molecular hybridization assays. Arch Virol. 1989;106(1-2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01311046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Nakagomi O. RNA-RNA hybridization identifies a human rotavirus that is genetically related to feline rotavirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1431–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1431-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi S. K., Olive D. M., Strannegard O. O., al-Nakib W. Molecular epidemiology of human rotavirus infections based on genome segment variations in viral strains. J Med Virol. 1988 Nov;26(3):249–259. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele A. D., Alexander J. J. The relative frequency of subgroup I and II rotaviruses in black infants in South Africa. J Med Virol. 1988 Mar;24(3):321–327. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L., Uhnoo I., Grandien M., Wadell G. Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus infections in Uppsala, Sweden, 1981: disappearance of a predominant electropherotype. J Med Virol. 1986 Feb;18(2):101–111. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Beards G. M., Flewett T. H. Serotyping and subgrouping of rotavirus strains by the ELISA test. Arch Virol. 1982;73(3-4):219–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01318076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White L., Perez I., Perez M., Urbina G., Greenberg H., Kapikian A., Flores J. Relative frequency of rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in Venezuelan children with gastroenteritis as assayed with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):516–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.516-520.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]