FIGURE 1.
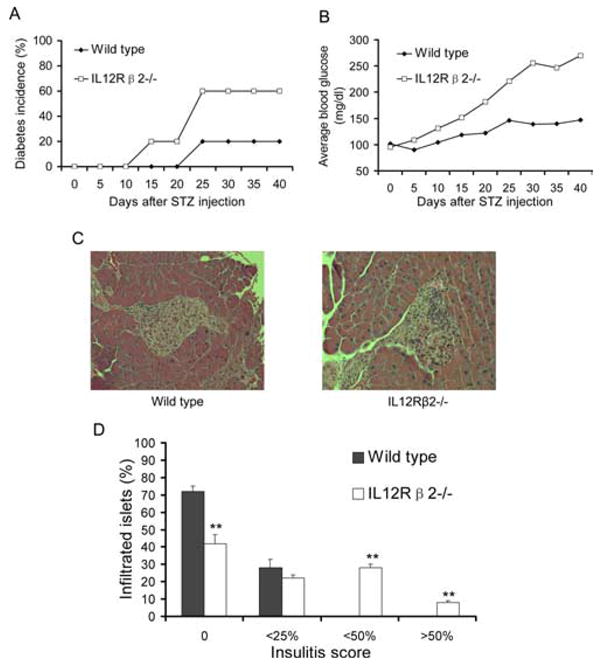
IL-12Rβ2−/− mice and susceptibility to STZ diabetes. IL-12Rβ2−/− mice and WT mice were injected i.p. with freshly made STZ at 50 mg/kg/day for 5 continuous days. Blood samples were harvested via the tail vein every 5 days after STZ injection, and plasma glucose levels were determined. Significantly hyperglycemic animals (plasma glucose >250 mg/dl) were considered diabetic. A and B, Diabetes incidence (A) and average level of blood glucose (B), n = 10 in each group. Mice were sacrificed 40 days after diabetes induction. Pancreatic sections were stained with H&E. C, WT mice with hyperglycemia (left) vs IL-12Rβ2−/− mice with hyperglycemia after STZ injection (right). D, Quantification of infiltrated islets and ranking of insulitis were performed. The degree of mononuclear cell infiltration (insulitis score) was measured using the following rankings: no infiltration (0), peri-insulitis (<25%), moderate insulitis (<50%), and severe insulitis (>50%). **, p < 0.01. One representative experiment of two is shown.
