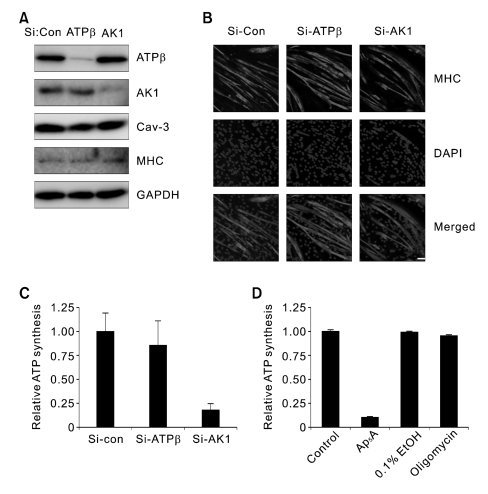
Figure 2.
AK1 is required for exATP synthesis in myotubes. (A) Si-Control (Si-Con), Si-AK1, or Si-ATP synthase β (Si-ATPβ) was treated in myoblasts that were further differentiated for 3 days. The whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ATP synthase β, AK1, Cav-3, and MHC antibodies. (B) Si-Con-, Si-ATPβ-, or Si-AK1-treated myotubes were analyzed by immunofluorescence with anti-MHC antibody. The myotubes were also stained with DAPI. The white bar indicates a length of 50 µm. (C) The exATP content was measured in the myotubes down-regulating AK1 or ATP synthase β after the cells were incubated with ADP (200 µM), Pi (20 mM), and MgCl2 (2 mM) for 1 min. ATP content was normalized by the protein concentration. (D) Myotubes that had been differentiated for three days were pretreated with 100 µM Ap5A or 20 µg/ml oligomycin for 30 min, and the exATP content was measured after the cells had been incubated with ADP (200 µM), Pi (20 mM), and MgCl2 (2 mM) for 1 min. Ethanol was used as a vehicle for oligomycin. The ATP content was normalized by the protein concentration.