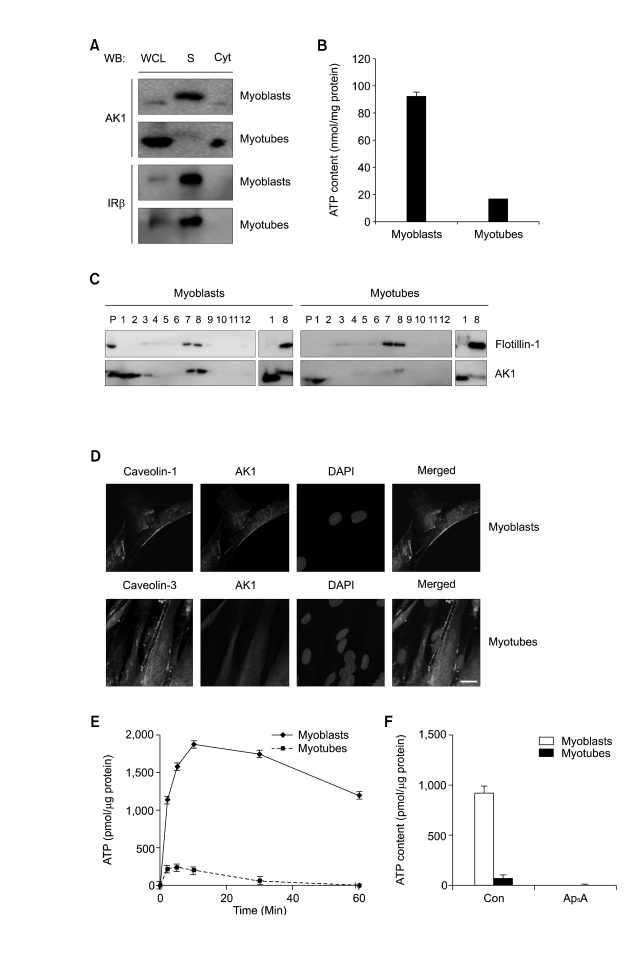
Figure 3.
AK1β was localized in the lipid rafts of myoblasts and diminished during myogenesis. (A) Myoblasts and 3-days-differentiated myotubes were fractionated into cytoplasm and sarcolemma (= plasma membrane of skeletal muscle). AK1 and insulin receptor β(IRβ were analyzed by immunoblotting. WCL, whole cell lysates; S, sarcolemma Cyt, cytoplasm. (B) ATP content was measured after incubating sarcolemma with ADP (200 µM), Pi (20 mM), and MgCl2 (2 mM) for 1 min. The ATP content was normalized by the protein concentration of sarcolemma. (C) Lipid rafts were isolated from myoblasts and myotubes, based on detergent insolubility and low density (Brown et al., 1992). After sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation, each fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-flotillin-1 and AK1 antibodies. Fraction number 1, and 2 represent non-raft fractions whereas fraction number 7, and 8 do raft fractions. P indicates pellet. Non-raft fraction (fraction number 1) and raft fraction (fraction number 8) were also analyzed by immunoblotting for side-by-side comparison of AK1 and AK1β with different molecular weights. (D) Co-localization of AK1 and Caveolin-1 in myoblasts and AK1 and Caveolin-3 in 3-days-differentiated myotubes was determined by immunofluorescence. The cells were also stained with DAPI. The white bar indicates a length of 10 µm. (E) ATP content was measured after incubating the lipid rafts of myoblasts or myotubes with ADP (200 µM), Pi (20 mM), and MgCl2 (2 mM) for the indicated amounts of time. The ATP content was normalized by the protein concentration of the lipid rafts. (F) The lipid rafts from myoblasts or 3-days-differentated myotubes were preincubated with Ap5A (100 µM) for 30 min, and were then incubated with ADP (200 µM), Pi (20 mM), and MgCl2 (2 mM) for 1 min before the measurement of ATP content. The ATP content was normalized by the protein concentration of the lipid rafts.