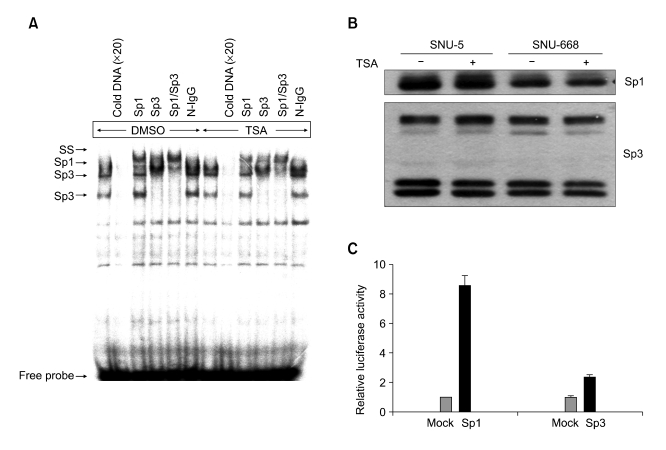
Figure 4.
Sp1 and Sp3 bind to the DLC-1 promoter and Sp1 is mainly involved in activation of the DLC-1 promoter by TSA. (A) Sp1/Sp3 binds to the Sp1 sites located within DLC1 promoter. EMSA was carried out using [γ-32P] ATP -labeled oligonucleotide spanning Sp1 binding sites of DLC1 promoter and nuclear extracts prepared from SNU-5 cells treated with DMSO or 330 nM TSA for 12 h. The reaction was carried out in the absence (lanes1 and 7) or presence of 20-fold molar excess of unlabeled probe (lanes2 and 8) or in the presence of specific antibodies to Sp1 (lanes3 and 9), Sp3 (lanes4 and 10), both (lanes5 and 11), or normal rabbit IgG (lanes6 and 12). (B) TSA has no effect on the expression of Sp1 and Sp3 protein. Protein extracts from DMSO-or 330 nM TSA-treated SNU-5 and SNU-668 cells were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies directed to Sp1 or Sp3. (C) Sp1 is the main transactivators of the DLC-1 promoter in response to TSA. Empty vector (mock), Sp1, or Sp3 expression vectors were cotransfected with the DLC-1 promoter luciferase construct (-219/+117-pGL3b) into SNU-668 cells and treated cells with 330 nM TSA for 12 h before measuring luciferase activity. Data are representative of two independent experiments performed in triplicate.