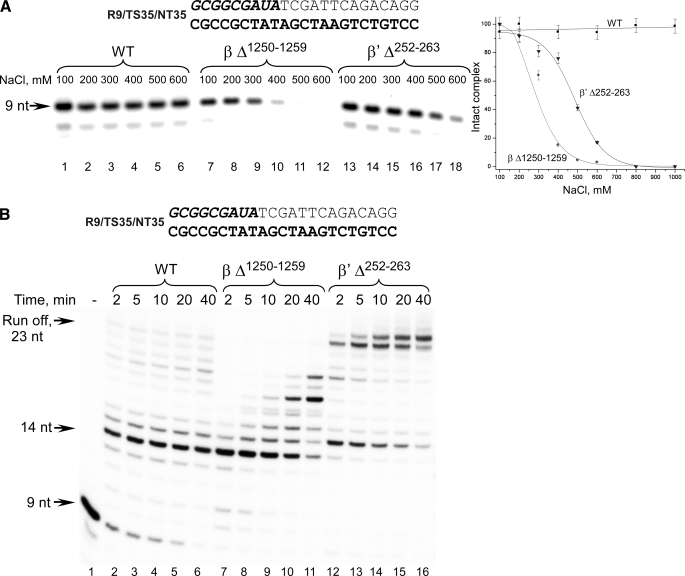
FIGURE 4.
Characterization of E. coli RNAPs having mutations in the RNA displacement region. A, mutant E. coli RNAPs form salt-sensitive ECs. ECs formed with the WT (lanes 1–6), βΔ1250–1259 (lanes 7–12), and β′Δ252–263 (lanes 13–18) mutant E. coli RNAPs were immobilized on nickel-agarose beads, incubated with different NaCl concentrations, washed with the transcription buffer, and analyzed by 20% PAGE containing 6 m urea. Dissociation of ECs is plotted as a function of salt concentration. Error bars represent S.D. calculated in three independent experiments. B, mutant E. coli RNAPs demonstrate different primer extension properties. ECs were formed using R9/TS35/NT35 scaffold. Runoff transcription assays were performed in the presence of 100 μm NTPs at 37 °C for the times indicated and analyzed as described above.