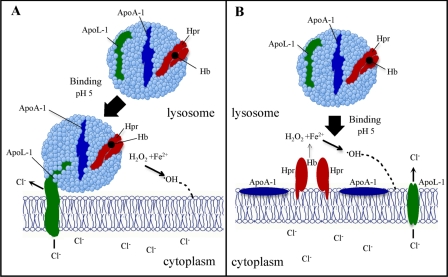
FIGURE 6.
Models of the interaction of TLF with the lysosomal membrane and proposed mechanism of TLF disruption of trypanosome lysosomal membranes. The stable integration of TLF into lipid bilayers may be facilitated by either a tethering (A) or a fusion (B) of the TLF particle into the membrane. Reduced Fe2+ from Hb, at low pH, in the presence of H2O2 results in the formation of membrane-reactive •OH. Insertion of apoL-1 into the membrane allows Cl– to enter from the cytoplasm. The synergistic activity of Hb, carried by Hpr, and the pore-forming activity of apoL-1 provides maximal lysosomal destabilization as based upon published results (5, 6). The dashed line represents the reaction of •OH with the lysosomal membrane.