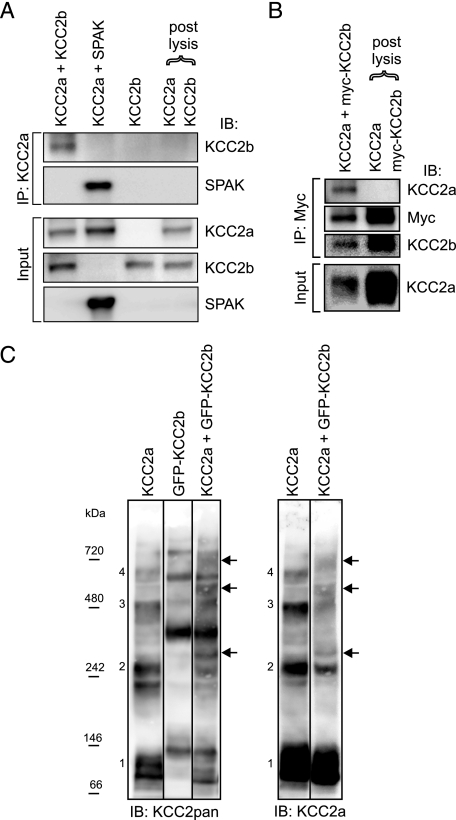
FIGURE 8.
KCC2a can interact with KCC2b in vitro. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and lysed 48 h later. A and B, the lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with the indicated antibodies and analyzed for interacting partners using standard SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (IB). A, after precipitation with the KCC2a antibody, immunoblotting with the KCC2b antibody detected a band of ∼140 kDa (corresponding to KCC2b) from cells coexpressing KCC2a and KCC2b but not from the combined lysate of cells expressing KCC2a and KCC2b separately (upper panel of IP:KCC2a part). Immunoblotting with the SPAK antibody confirmed that KCC2a is able to interact with SPAK (lower panel of IP: KCC2a part). Analysis of the lysates (Input) ensured that the proteins were successfully expressed. B, after precipitation with an anti-Myc antibody, immunoblotting with the KCC2a antibody detected a band corresponding to KCC2a from cells coexpressing KCC2a and Myc-KCC2b fusion construct but not from the combined lysate of cells expressing KCC2a and Myc-KCC2b separately (upper panel of IP:Myc part). Expression of KCC2a in the cell lysates is also shown (Input). For simplicity, only the monomer bands of KCC2 are shown in A and B. C, the lysates were separated in native PFO gel and analyzed by immunoblotting sequentially with KCC2pan (left panel) and KCC2a (right panel) antibodies. Bands corresponding to the expected size of monomeric (band 1) and homo-oligomeric (band 2–4) forms of KCC2a are numbered. The corresponding bands for the GFP-KCC2b fusion protein are larger due to the additional GFP moiety (∼30 kDa). Bands corresponding to the expected size of hetero-oligomers between KCC2a and GFP-KCC2b (marked by arrows) are seen between the KCC2a and GFP-KCC2b homo-oligomeric bands, and they appear more prominent in the left than in the right panel because the KCC2pan antibody can bind both KCC2a and GFP-KCC2b in the hetero-oligomers.