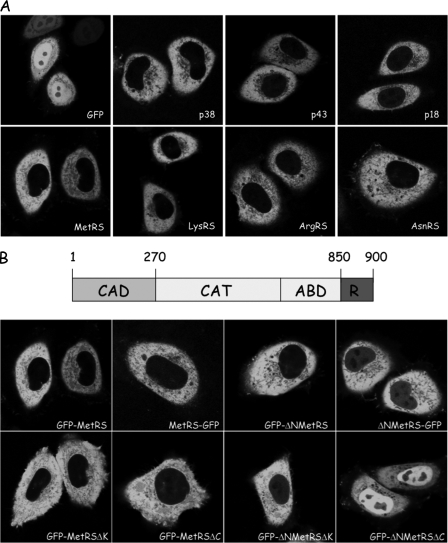
FIGURE 1.
Subcellular localization of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in human cells. A, localization of GFP, of components of MARS (p38, p43, p18, MetRS, LysRS, and ArgRS), and of a representative of free enzymes (AsnRS) expressed in HeLa cells after transient transfection with pEGFP derivatives. B, subcellular localization of MetRS and of truncated derivatives. The structural organization of human MetRS is indicated above. CAD, the N-terminal, eukaryotic-specific complex association domain; CAT, the conserved catalytic domain; ABD, the conserved anticodon-binding domain; R, the eukaryotic-specific, repeated domain appended to the C terminus and containing an additional four-lysine cluster at the very C terminus (30). HeLa cells were transiently transfected with pEGFP-N1 or pEGFP-C1 plasmids expressing fusion proteins with MetRS (GFP-MetRS and MetRS-GFP, according to the polarity of the fusion), MetRS with a deletion of its N-terminal, eukaryotic-specific domain (GFP-ΔNMetRS and ΔNMetRS-GFP), with a deletion of its C-terminal, lysine-rich cluster (GFP-MetRSΔK), with a complete deletion of its C-terminal, helix-turn-helix domain (GFP-MetRSΔC), or with a combination of N- and C-terminal deletions (GFP-ΔNMetRSΔK and GFP-ΔNMetRSΔC). The cellular localization of GFP alone or of the fusion proteins was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. All of the images represent equatorial sections of the nuclei.