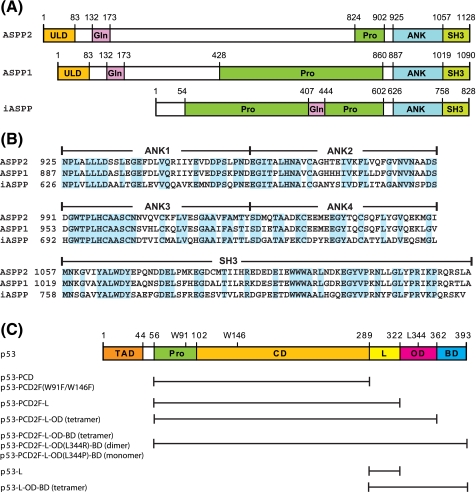
FIGURE 1.
Amino acid sequences and domain organization of ASPP and p53 proteins. A, domain organization of ASPP2, ASPP1, and iASPP. Individual domains are as follows: ubiquitin-like (ULD), glutamine-rich (Gln), proline-rich (Pro), ankyrin repeats (ANK), and Src homology 3 (SH3). B, sequence alignment of the C-terminal regions of ASPP2, ASPP1, and iASPP. Identical residues are highlighted in cyan. The domain boundaries are indicated at the top of the protein sequences. C, domain organization of p53. Individual domains are the transcription activation (TAD), the proline-rich (Pro), the DNA binding or core (CD), the linker (L), the oligomerization or tetramerization (OD), and the basic (BD) domains. All p53 protein constructs used in the present study are listed: p53-PCD (residues 56-289), p53-PCD2F (residues 56-289 with W91F and W146F), p53-PCD2F-L (residues 56-322 with W91F and W146F), p53-PCD2F-L-OD (residues 56-362 with W91F and W146F), p53-PCD2F-L-OD-BD (residues 56-393 with W91F and W146F), p53-PCD2F-L-OD(L344R)-BD (residues 56-393 with W91F, W146F, and L344R), p53-PCD2F-L-OD(L344P)-BD (residues 56-393 with W91F, W146F, and L344P), p53-L (residues 289-322), and p53-L-OD-BD (residues 289-393).