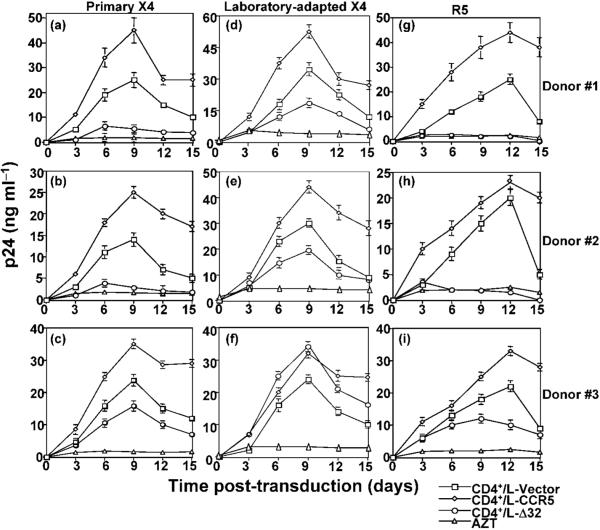
Fig. 6.
Resistance of CD4+ T lymphocytes isolated from PBMC lines to R5 and primary X4 but not to laboratory-adapted X4. CD4+ T lymphocytes were isolated from immortalized/transduced PBMCs using magnetic beads, washed several times in complete medium and infected with primary X4 (a-c), the laboratory-adapted X4 IIIB (d-f) or R5 Ba-L (g-i). Infections were performed using 10 ng p24 ml-1 of the indicated HIV-1 isolate. Culture fluids were harvested every 3 days and replaced with fresh medium. The amount of p24 antigen in the cell-containing supernatants was measured by ELISA. As a negative control for HIV infection, azidothymidine (AZT) was added at a final concentration of 10 μM to infected cells and maintained throughout the course of infection; AZT is a nucleoside analogue antiviral drug that inhibits the replication of retroviruses such as HIV by blocking the enzyme reverse transcriptase.