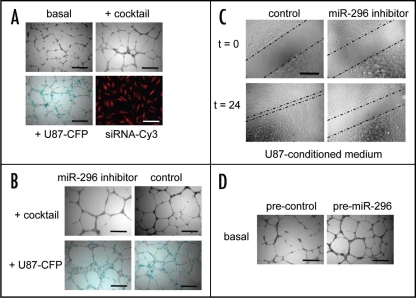
Figure 2.
miR-296-mediated induction and inhibition of angiogenesis. (A) HBMVEC cells were cultured on Matrigel-coated plates in basal medium (EBM; Cambrex) only, basal medium supplemented with a cocktail of angiogenic factors (EGM), or with U87-human glioma cells expressing the cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) in order to induce miR-296 and tubule formation. Transfection efficiency of endothelial cells in monolayer culture was determined (>99%) by using siRNA-Cy3 molecules. (B) HBMVECs were transfected with miR-296 inhibitor or non-related control molecules and analyzed for tubule formation. At 48 hr after inhibition of U87 or cocktail-induced miR-296, less chaotic tubule networks were observed. (C) HBMVECs were transfected with anti-miR-296 inhibitor or non-related control molecules and analyzed for migration capacity. Inhibition of miR-296 resulted in a significant decrease in migration. (D) Overexpression of miR-296 at 24 hr after transfection of premiR-296 molecules resulted in increased angiogenesis in vitro. Size bars, 300 µm (Adapted from Würdinger et al. Cancer Cell 2008).76