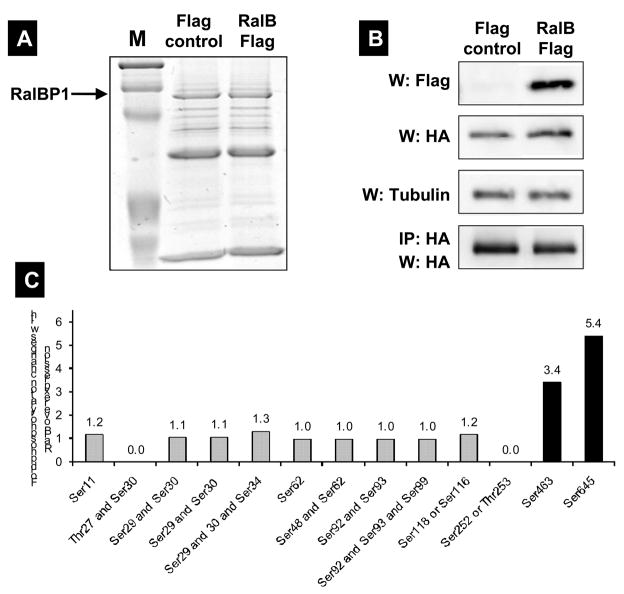
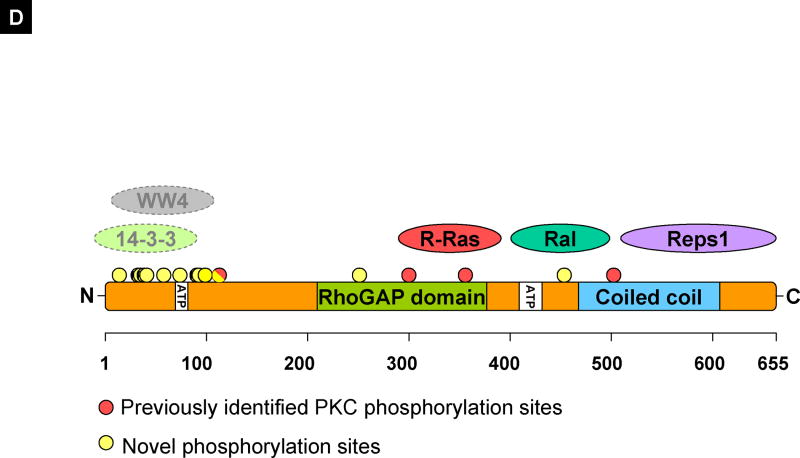
Figure 4.
(A) RalBP1 was precipitated from 293T cells transiently transfected with RalBP1-HA with Flag control vector or RalB-Flag and detected with coomassie blue staining. (B) Western (W) blot or IP for Flag or HA indicating expression of RalBP1-HA and RalB-Flag in corresponding samples. (C) Phosphorylation changes in RalBP1-HA in 293T cells overexpressing wild type RalB. Only sites S463 and S645 show significant change in phosphorylation levels between mock and RalB-transfected cells. (D) RalBP1 structural domains include RhoGAP and the coiled coil at aa 207–373 and 469–610 respectively (http://elm.eu.org/). ATP binding sites (aa 65–80 or 415–448) [16]. Putative interaction partners are schematically depicted. Previously suggested PKC phosphorylation sites are in red and include 118S, 297T, S353 and S509 [17]. Phosphorylation sites described here are in yellow and include S11, T27, S29, S30, S34, S48, S62, S92, S93, S99, S116 or S118, S252 or T253 and S463. S118 is indicated as half red and half yellow. Putative binding proteins 14-3-3 and WW4-binding proteins shown in computationally assigned locations.