Figure 9.
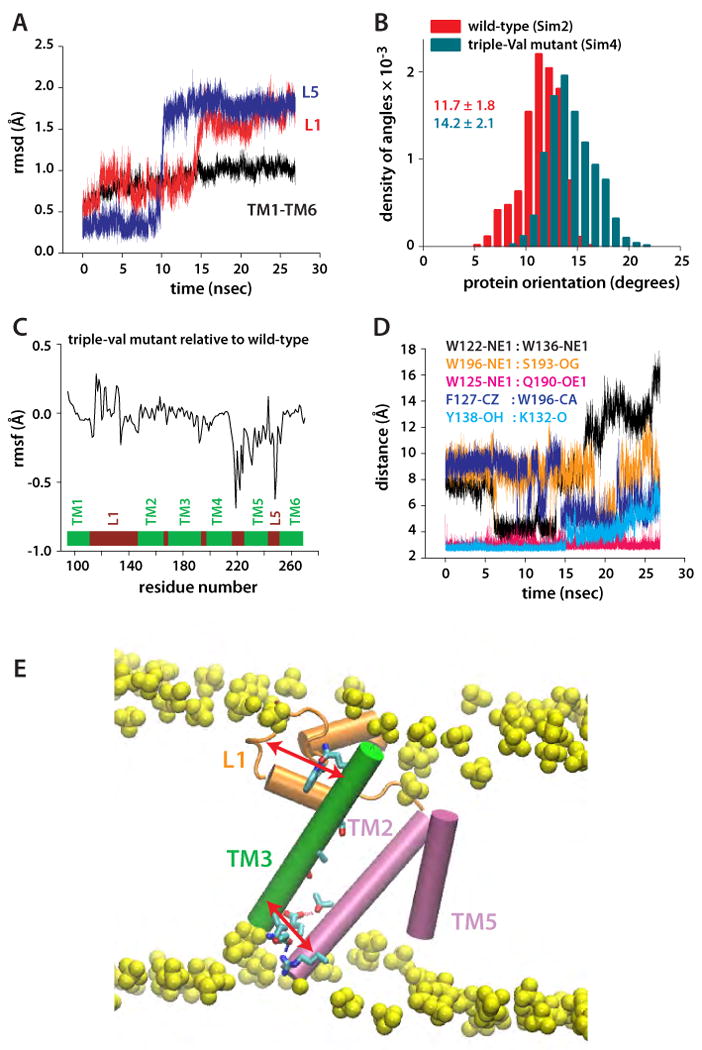
Protein orientation and dynamics of the triple-Val mutant (W236V/F232V/L229V). (A) Rmsd of TM1-TM6 and of loops L1 and L5, relative to the starting coordinates. The spontaneous and nearly simultaneous switching of L1 and L5 suggest conformational coupling between TM2/TM5 and L1. (B) Orientation of triple-Val GlpG (compare with Figure 7A). (C) Changes in the rmsf of triple-Val GlpG relative to the wild-type are observed not only in the region of TM5, but also in L1. (D) Dynamics of selected intra-protein interactions in Sim4 indicating that perturbation of TM5 is transmitted to L1. (E) Suggested relay mechanism in GlpG. Due to the array of H-bonds along TM3 (green), this structural element can act as a rigid arm that relays perturbations between L1 (orange) and the TM2/TM5 helices (orange) through intra-helical and L1:TM3 H-bonding.
