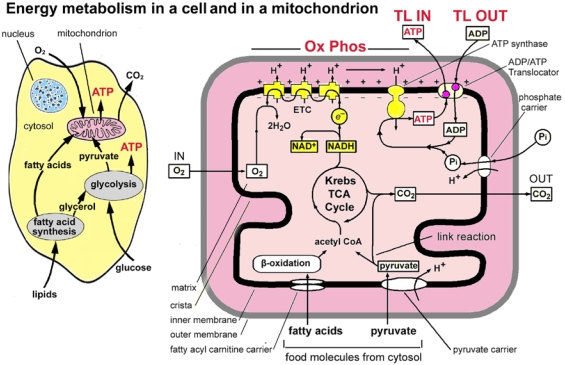
Figure 1.
Main stages and location of energy metabolism in a human cell (left), and simplified details of a mitochondrion showing the main metabolic cycles and the oxidative phosphorylation respiratory chain (right). The outer mitochondrial membrane is highly permeable whereas the inner membrane is permeable only to water and gases. Special carrier and Translocator proteins pass reactants through it. At the top are the proteins involved in the respiratory electron transfer chain (ETC) and in the transfer of ATP and ADP between the cytosol and mitochondrion. ADP and Pi are combined by ATP synthase to make ATP. The ADP/ATP Translocator opens OUT to transfer ADP into the matrix and opens IN to transfer ATP to the cytosol. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide plays a key role in its oxidised form NAD+ and its reduced form NADH + H+ in carrying and transferring protons (H+) and electrons (e−). Adapted from: [35] and [5].