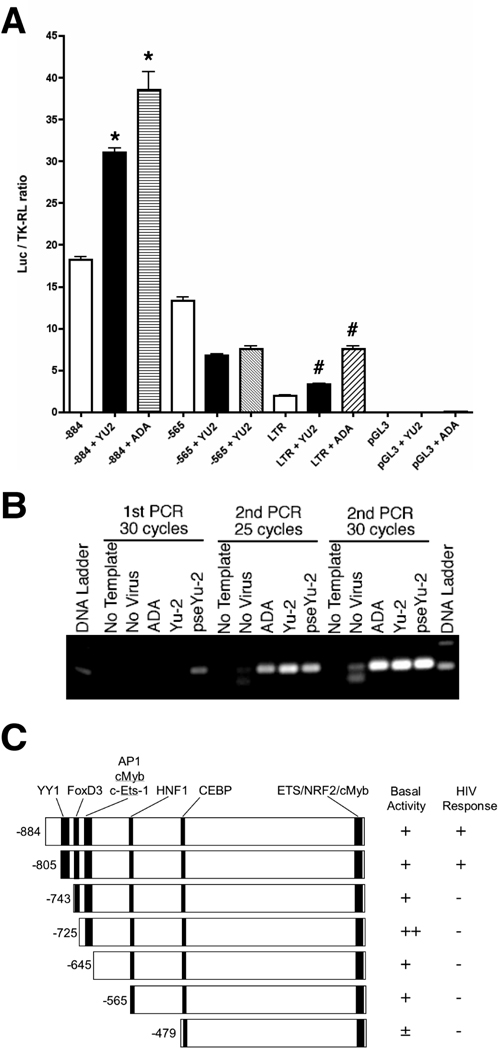
Figure 1. OTK18 promoter luciferase reporter gene induction and viral infection of a human cell line.
A. Cells were transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid pGL3-(−884/+1), pGL3-(−565/+1), pHIV-LTR-Luc, or control pGL3 with pTK-RL (thymidine kinase promoter-driven Renilla luciferase expression vector), and infected with VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1YU2 (YU2, 2,500 cpm/ml) or HIV-1ADA (ADA, 2,500 cpm/ml). Dualluciferase assays were performed at 48 hrs after the infection. The results were shown as luciferase activity/TK-RL activity ratio. * denotes p < 0.01 as determined by ANOVA and Newman Keuls post-hoc, respectively. B, Detection of HIV DNA after viral infection. Cells were infected with non-pseudotyped ADA (10,000 cpm/ml), Yu-2 (2,500 cpm/ml), and pseudotyped Yu-2 (pseYu-2), and genomic DNA was isolated at 24 hr after infection. The samples were subjected to 2 rounds of PCR against proviral gag sequence as described (30 cycles in 1st round and 25 or 30 cycles in 2nd round). C, Schematic presentation of OTK18 promoter response elements (YY1, FOXD3, cMyb/AP1, C/EBP, c-Ets-1, NRF, cMyb), design of deletion mutants (−884/+1, −805/+1, −743/+1, −725/+1, −645/+1, −565/+1, and −479/+1), and results of basal luciferase activity and induction by pseudotyped YU2 infection.