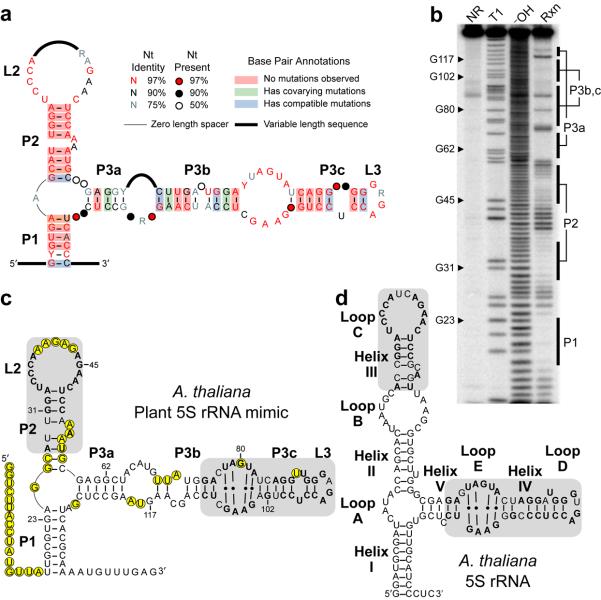
Figure 1.
A conserved structured RNA element in plants resembles 5S rRNA. (a) Consensus sequence and secondary structure model for the angiosperm representatives of an RNA element identified by comparative bioinformatics. Sequences of all representatives are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. Calculations for nucleotide conservation and base pair annotations were performed as previously described49. (b) In-line probing analysis of the 5′ 32P-labeled RNA shown in c, which encompasses the A. thaliana representative of the RNA element (nucleotides 649-793 of AtTFIIIA gene, NCBI gi 42592260). NR, T1, and −OH designate lanes containing nonreacted RNA, or RNA subjected to partial digest with RNase T1 (G-specific) or alkali, respectively. Rxn identifies RNA subjected to in-line probing. Labeled bars identify regions corresponding to pairing elements shown in c. (c) Sequence and secondary structure model for the A. thaliana plant 5S rRNA mimic. Positions with substantial backbone cleavage 3′ to the nucleotide upon in-line probing are circled. Shaded regions have sequence and structural similarity to corresponding shaded regions in A. thaliana 5S rRNA shown in d, with identical nucleotides in bold. Numbered nucleotides match labeled G nucleotides in b. (d) Sequence and secondary structure for the A. thaliana representative of 5S rRNA. Structural elements (helices and loops) are labeled using the 5S rRNA naming convention30. Shaded regions and bolded nucleotides are defined in c.