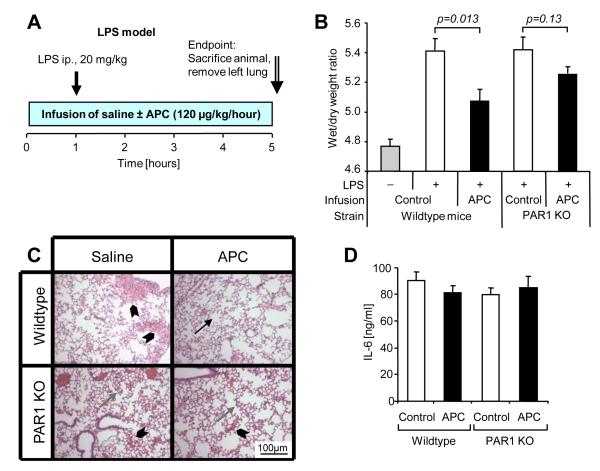
Figure 6. Infusion of APC reduces pulmonary fluid accumulation in a mouse endotoxemia model dependent on PAR1.
A) Male C57BL/6 wildtype or PAR1-deficient (PAR1 KO) mice were infused with either saline alone or with murine APC (120 μg/kg/h) for 5 h via a central venous catheter (10-12 mice per group). LPS (20 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally one hour after the start of the infusion. Lungs were dissected for wet/dry weight ratio determination at the end of the infusion period. B) Lung wet weight/dry weight ratios are shown (means±SEM, P values indicated). Results from non LPS injected animals are shown as a reference. C) Hematoxylin-Eosin stained representative pulmonary tissue sections show normal alveolar tissue (arrow) alveolar edema (gray arrow) and alveolar flooding (arrowhead). D) IL-6 plasma levels at the end of the infusion are shown (means±SEM).