Fig. 3.
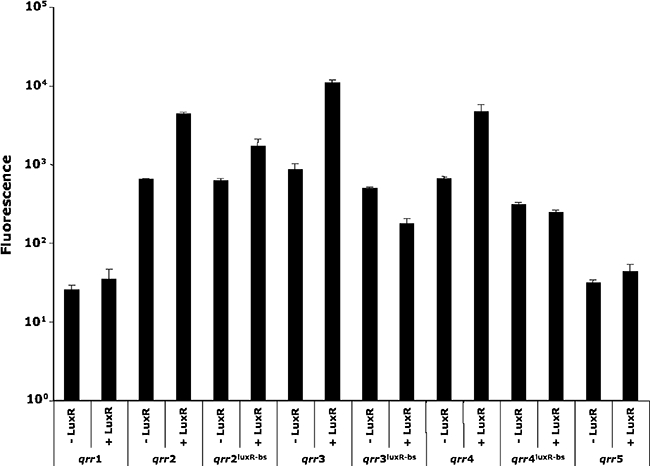
LuxR directly activates transcription of qrr2, qrr3 and qrr4 in E. coli. The constitutively active luxO allele, luxOD47E, was recombined onto the chromosome of E. coli strain MC4100 at the λatt site. Flow cytometry was used to measure fluorescence production (in arbitrary units) from WT V. harveyi qrr promoter-gfp fusions and the qrr promoters with the LuxR-binding sites mutated (qrrluxR-bs). The measurements were made in the presence and absence of LuxR. E. coli strains: KT1646 (qrr1-gfp), KT1648 (qrr1-gfp + luxR), KT1529 (qrr2-gfp), KT1530 (qrr2-gfp + luxR), KT1535 (qrr2luxR-bs-gfp), KT1536 (qrr2luxR-bs-gfp + luxR), KT1531 (qrr3-gfp), KT1532 (qrr3-gfp + luxR), KT1614 (qrr3luxR-bs-gfp), KT1615 (qrr3luxR-bs-gfp + luxR), KT1533 (qrr4-gfp), KT1534 (qrr4-gfp + luxR), KT1539 (qrr4luxR-bs-gfp), KT1540 (qrr4luxR-bs-gfp + luxR), KT1647 (qrr5-gfp), KT1649 (qrr5-gfp + luxR). Background fluorescence was measured in the absence of LuxO˜P which averaged around 20 units (data not shown). Cultures were grown in triplicate and error bars denote standard deviation of the mean.
