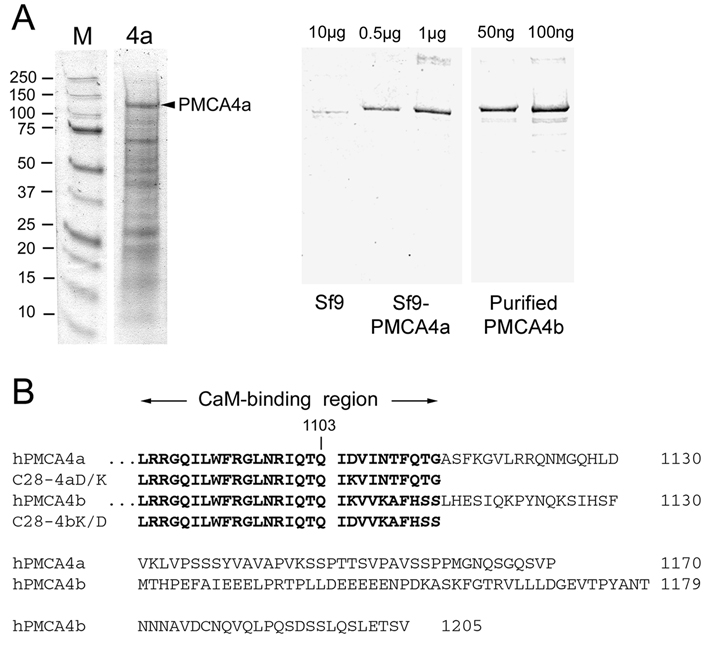
FIGURE 1. Quantification of PMCA4a in microsomes from baculovirus-infected insect cells and amino acid sequence comparison of the COOH-terminal tails of human PMCA4a and 4b.
A. Left panel: Coomassie Blue stained gel of microsomal membrane proteins (5 µg) from Sf9 cells expressing PMCA4a. Molecular size standards are shown on the left with their masses given in kDa. PMCA4a (arrowhead) migrates at ~130 kDa. Right panel: Quantification of PMCA4a expression in Sf9 cell membranes by Western blotting. 10 µg of uninfected Sf9 cell membranes were electrophoresed next to 0.5 µg and 1 µg of PMCA4a-expressing Sf9 membranes and 50 ng and 100 ng of purified PMCA4b as standards. Western blotting for PMCA was performed with antibody 5F10 as described (17). PMCA4a amounts to ~5% of the Sf9 microsomal protein as determined by Western blotting and densitometry (13). B. Sequence comparison of human PMCA4a and PMCA4b starting with the CaM binding region. The last common residue (1103) preceding the alternative splice site is indicated. The sequences of the CaM-binding peptides C28-4a and C28-4b, and of the single-residue mutant peptides C28-4aD/K and C28-4bK/D are indicated in bold print.