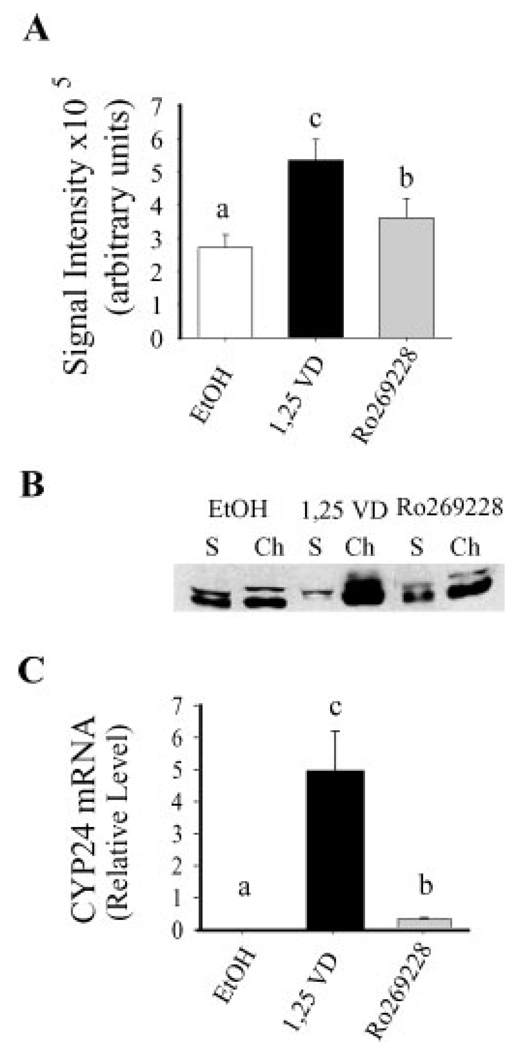
Fig. 6.
The ability of VDR ligands to stimulate VDR nuclear import in parental Caco-2 cells is associated with their transcriptional efficacy. (A) The effect of 5 min treatment with 100 nM 1,25(OH)2D3, 100 nM Ro269228, or vehicle (EtOH) on GFP-VDR nuclear import. Bars represent mean±SEM(n=6). (B) The effect of 1 h treatment with 100 nM 1,25(OH)2D3, Ro269228, or vehicle (EtOH) on the association of endogenous VDR with chromatin. The figure is representative data from a single sample per treatment group. S, soluble; Ch, chromatin. (C) The effect of a pulse treatment (5 min treatment, 7 h 55 min vehicle) with either 100nM1,25(OH)2D3, Ro269228, or vehicle (EtOH) on CYP24 mRNA levels as determined by RT-PCR analysis. CYP24 mRNA levels are normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels within the samples. Bars represent mean±SEM (n=3 per treatment); the experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Values with different superscripts are significantly different from one another (P<0.05).