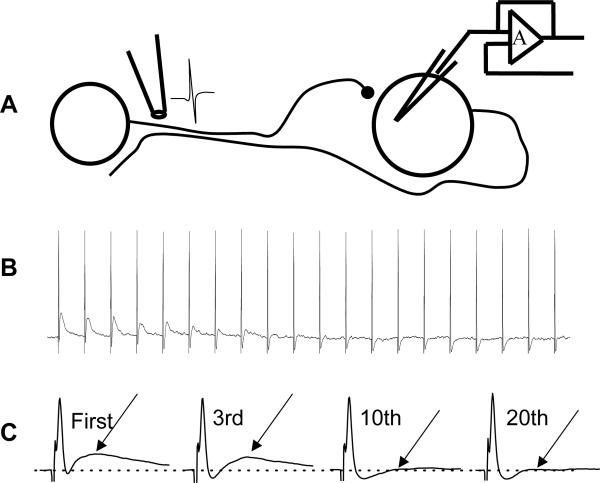
Fig. 8.
Action potential failure did not contribute to synaptic rundown. (A) Diagram of experiment set-up used to evaluate action potential failure during trains of stimulation. The focal stimulating electrode was positioned on an internodal strand that contained the axon of the neuron from which intracellular recordings were obtained. The strand also contained nerve fibers providing synaptic input to the same neuron. (B) Recording of antidromic action potentials and fEPSPs elicited by a 10 Hz train of stimulation. The fEPSP declined in amplitude while the antidromic action potential followed each stimulus in the train. (C) Examples of the antidromic action potential and fEPSPs shown on an expanded time scale.