Fig. 2.
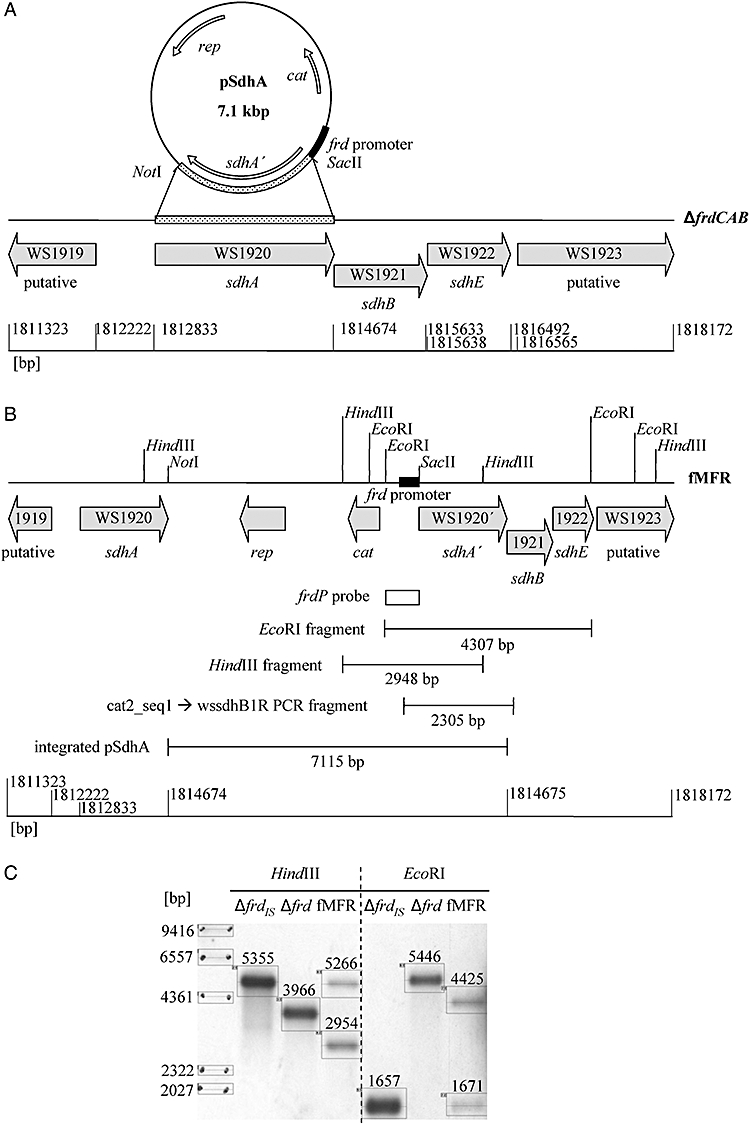
Genetic system for the production and manipulation of the SdhABE complex. A. In the vector pSdhA the structural gene sdhA is cloned next to the strong frd promoter (black box). The vector integrates via the homologous sdhA gene (dotted boxes) at the native locus in the genome of the QFR-deficient deletion strain ΔfrdCAB. B. In the resulting mutant fMFR the sdhABE operon is under control of the strong frd promoter. This system allows introduction of mutations and affinity tags in sdhA. Open reading frames are indicated by grey arrows including locus tags. The ruler gives base pairs with respect to the Wolinella succinogenes DSM 1740 complete genome sequence (NC_005090). Correct integration was verified via PCR with the primer pair Cat2_seq1 and wssdhB1R and sequencing of the resulting DNA fragment and Southern blot. C. Southern blot of cut genomic DNA from mutants fMFR and ΔfrdCAB. The frdP probe (clear box) hybridizes with the frd promoter and detects the 4307 bp EcoRI and the 2948 bp HindIII fragment, respectively, in the mutant fMFR. The probe also detects the frd promoter at its native locus (second bands in lanes fMFR). An insertion of a 1.3 kb insertion sequence is known to occur in the genome of the deletion mutant upstream of the kan gene that replaces the frdCAB genes [IS1302, see Simon and Kröger (1998) for details]. Consequently both variants with and without insertion sequence were used as positive control (lanes ΔfrdIS and Δfrd respectively). IS1302 also introduces an additional EcoRI restriction site leading to a smaller EcoRI fragment in ΔfrdIS than in Δfrd. Fragment sizes were calculated from a calibration curve with the five marker bands using the program un-scan-it™ (Silk Scientific).
