Figure 4.
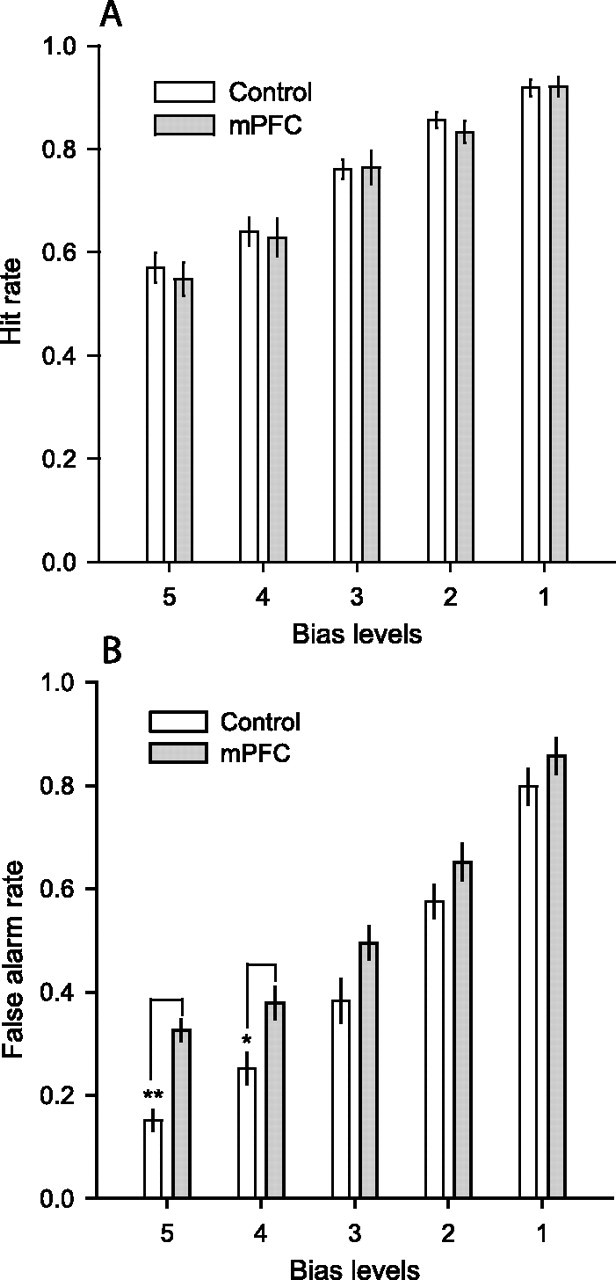
Hit and false alarm rates for control subjects and rats with medial prefrontal damage. The hit rates (A) and false alarm rates (B) are shown for each response bias level (1–5). The increase in false alarm rate was particularly large at the more conservative bias levels (bias 5, **p < 0.001; bias 4, *p < 0.05). There was no effect of the lesion on the hit rate at any bias level. Error bars show SEM.
