Figure 1.
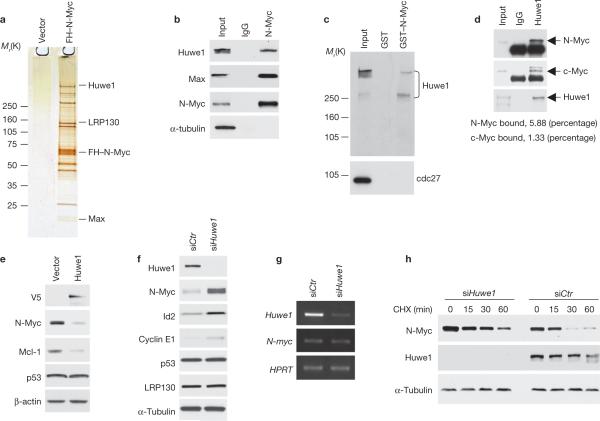
Huwe1 binds N-Myc in vivo and controls N-Myc stability. (a) Identification of Huwe1 in N-Myc complexes from human neuroblastoma cells. Silver staining of affinity purified FH–N-Myc complexes from IMR32 cells. Specific N-Myc-interacting proteins were identified by mass spectrometry and are indicated. (b) Lysates from IMR32 cells were immunoprecipitated with an anti-N-Myc antibody or normal mouse IgG (IgG). Western blotting was performed using anti-Huwe1, anti-Max and anti-N-Myc antibodies. α-tubulin is shown as a negative control for binding. Input is 1/100th of total extracts. (c) Lysates from IMR32 cells were mixed with GST or GST–N-Myc fusion proteins. Bound proteins were analysed by western blotting for Huwe1 or cdc27. Input is 1/50. Molecular markers are indicated on the left. (d) Lysates of U2OS cells stably expressing N-Myc were immunoprecipitated with antibodies directed against Huwe1 or rabbit IgG (IgG). Immunoprecipitates were resolved on SDS–PAGE and analysed by western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Input is 1/250. The percentage of cellular N-Myc and c-Myc associated with Huwe1 is indicated. (e) IMR32 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing the V5-tagged full-length Huwe1 or the empty vector. The levels of endogenous N-Myc, p53 and Mcl-1 were examined by immunoblotting. The V5 antibody was used to detect exogenously expressed Huwe1. (f) IMR32 cells were transfected with control (siCTR) or Huwe1 (siHuwe1) siRNA. Lysates were analysed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. (g) Parallel samples were analysed for gene expression by semi-quantitative RT–PCR. (h) IMR32 cells were transfected with control (siCTR) or Huwe1 (siHuwe1) siRNA and treated with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times. α-tubulin is shown as a control for loading. Full scans of immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Information, Fig. S9.