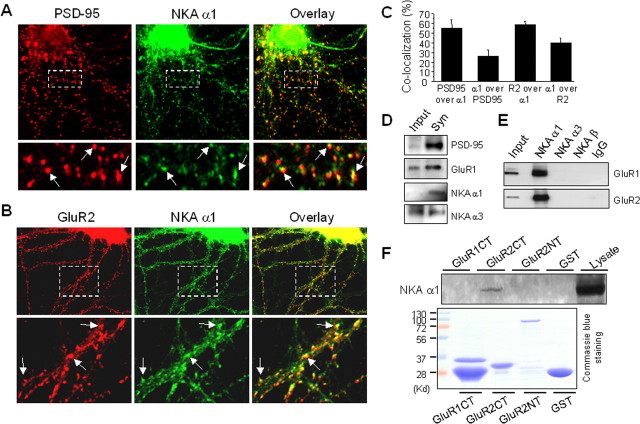
Figure 1.
NKA is enriched in synapses and associates with AMPARs. A, Cultured cortical neurons were fixed and immunostained under permeabilized conditions. The top panel is a representative neuron double-labeled with antibodies against the synaptic marker protein PSD-95 (monoclonal, 1:500) and the NKA α1 subunit (polyclonal, 1:300). PSD-95 showed a typical punctate pattern indicating its synaptic localization. The NKA α1 subunit immunofluorescence was distributed over the whole cell, with stronger intensity at the soma. Note that in the dendrites, NKA (green) forms clusters that were colocalized with PSD-95 (red) as indicated in the merged image (overlay), indicating synaptic enrichment of NKA. A selected region was enlarged (bottom) for clarity. Arrows indicate synaptic clusters with strong colocalization (yellow). B, Double staining of NKA and AMPARs. Under permeant conditions, cortical neurons were incubated with antibodies against NKA α1 subunits (polyclonal, 1:300), and GluR2 subunits (monoclonal, 1:300). A representative neuron was shown in separate channels (GluR2 in red, NKA α1 in green) and overlay (top). A boxed area was enlarged for clarity (bottom). Arrows indicate sites of colocalization. C, Quantification of pixel colocalization of NKA α1 with PSD-95 or GluR2. D, NKA in synaptosome. Synaptosome lysate prepared from rat cortical tissue was separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with different antibodies. Whereas both NKA α1 and α3 subunits were detected in synaptosome, α1 showed higher degree of enrichment. E, Coimmunoprecipitation of NKA and AMPARs. Rat brain cortical tissue was homogenized manually in lysis buffer and further solubilized for 1 h. Equal amounts of supernatant (500 μg/500 μl) were incubated with antibodies against the NKA α1, α3 or β subunits (3 μg each), or rabbit IgG (3 μg) as control. After protein A beads incubation and precipitation, the protein complexes were probed with anti-GluR1and reprobed with anti-GluR2 antibodies. F, GST pulldown assays. GST fusion proteins (20 μg) of C-terminals of GluR1 (GluR1CT) and GluR2 (GluR2CT), and of GluR2 N-terminal (GluR2NT) were incubated with cortical brain lysate (800 μg). GST alone was used as control. Pellets of GST pulldown were examined by Western blotting using anti-NKA α1 antibodies (top). A parallel gel was stained by Coomassie blue to confirm the loading of fusion proteins (bottom).