Figure 2. ZC3H14splice variants can be detectedin vivo.
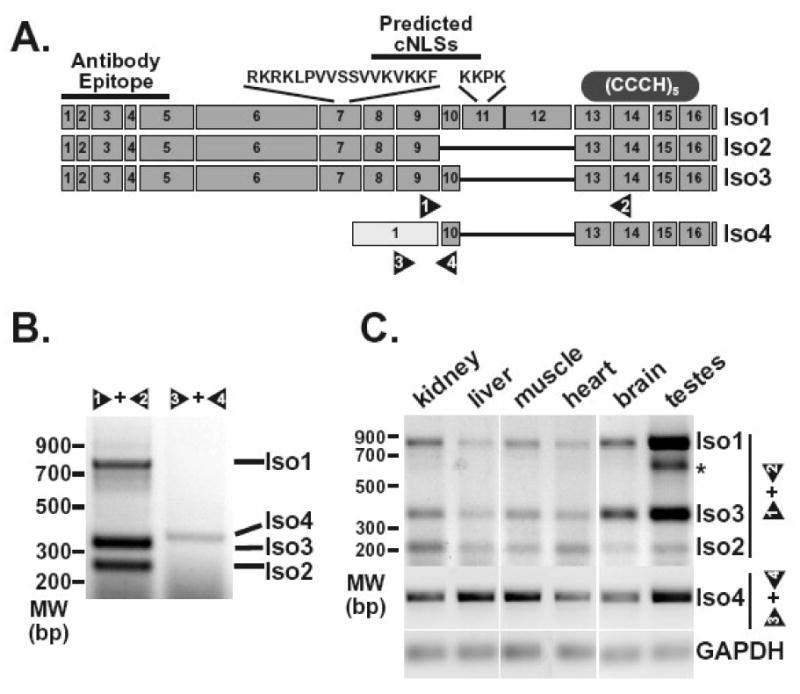
A. The diagram depicts exons predicted for the ZC3H14 splice variants encoding ZC3H14 isoform 1 (Iso1), isoform 2 (Iso2), isoform 3 (Iso3), and isoform 4 (Iso4). The sequences and approximate positions of predicted classical NLS motifs (cNLSs) are indicated at the top of the diagram. The location of the antibody epitope used to generate the polyclonal ZC3H14 antibody is also indicated as is the approximate location of the tandem Cys3His zinc finger domain (CCCH). Positions of primer pairs (1 and 2, 3 and 4) used to detect the splice variants are indicated at the bottom of the diagram. B. RT-PCR reactions (30 cycles) were performed on RNA isolated from HEK293 cells as described in Materials and Methods. Transcripts corresponding to ZC3H14 isoforms 1, 2, and 3 (Iso1, Iso2, Iso3) were detected using primer pair 1 and 2. Primer pair 3 and 4 was used to amplify the transcript corresponding to ZC3H14 isoform 4 (Iso4). Positions of the products corresponding to each splice variant are indicated. An additional band identified in the testes sample is indicated by the asterisk. This band likely reflects a ZC3H14 splice variant with additional alternative splicing of exons 10, 11, and 12. C. RT-PCR reactions were performed on RNA isolated from the mouse tissues indicated (kidney, liver, muscle, heart, brain, and testes). Isoform 1, 2 and 3 transcripts (Iso1, Iso2, Iso3) were detected using mouse primer pair 1 and 2 (see Figure 2A) with 30 cycles of amplification while the isoform 4 transcript (Iso4) was detected using mouse primer pair 3 and 4 with 60 cycles of amplification. The GAPDH transcript was amplified as a control for each tissue sample.
