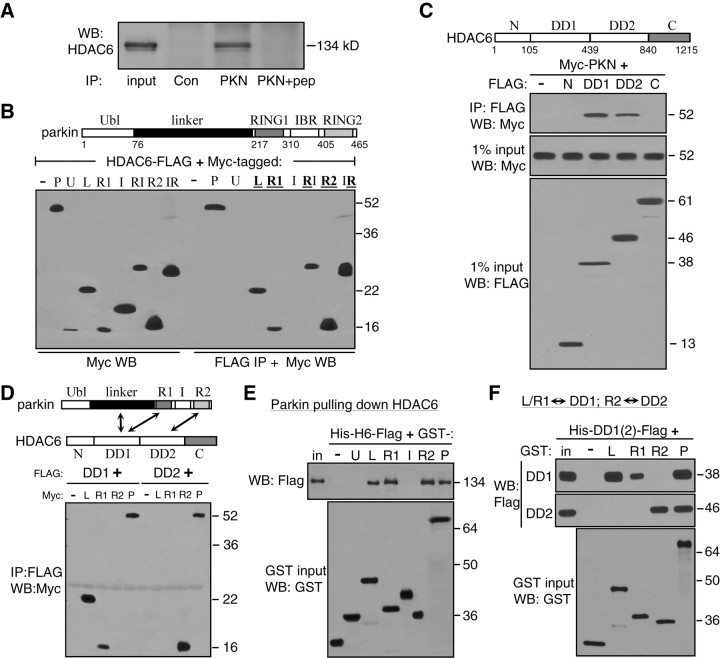
Figure 3.
Multiple interaction domains mediate direction binding between HDAC6 and parkin. A, Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous parkin and HDAC6 in SH-SY5Y cells. Cleared lysates were immunoprecipitated with an irrelevant antibody (Con), parkin antibody (PKN) or the parkin antibody with its antigenic peptide (PKN+pep). Immunoprecipitates and 1% of input were Western blotted with anti-HDAC6. B, Domains of parkin responsible for binding HDAC6. Myc-tagged parkin constructs as shown in the diagram were transfected with HDAC6-FLAG in HEK293T cells. FLAG immunoprecipitates and 1% input from cleared cell lysates were blotted with anti-Myc. HDAC6-FLAG coimmunoprecipitated with full-length parkin (P) or its L, R1 or R2 domains, but not with U or IRB (I) domain. The RI (R1+IBR) or IR (IBR+R2) construct was also coimmunoprecipitated with HDAC6. C, Domains of HDAC6 responsible for binding parkin. FLAG-tagged HDAC6 constructs as shown in the diagram were transfected with Myc-parkin in HEK293T cells. FLAG immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-Myc. Parkin coimmunoprecipitated with either DD1 or DD2 of HDAC6, but not the N-terminal or C-terminal domain of HDAC6. Total cell lysates were also blotted with anti-FLAG or anti-Myc to show expression levels of HDAC6 or parkin constructs, respectively. D, Coimmunoprecipitation between interaction domains of HDAC6 and parkin as indicated in the diagram. FLAG-tagged DD1 or DD2 domain of HDAC6 was transfected without (−) or with Myc-tagged HDAC6-binding domains of parkin (L, R1 or R2) or full-length parkin (P). FLAG immunoprecipitates were blotted with anti-Myc. DD1 domain of HDAC6 coimmunoprecipitated with L or R1 domain of parkin, while DD2 domain of HDAC6 coimmunoprecipitated with the R2 domain of parkin. E, Direct binding of purified parkin domains with purified HDAC6 in vitro. GST-tagged parkin domains were purified from E. coli and immobilized on glutathione beads, which was incubated with bacterially purified Hisx6-HDAC6-FLAG (His-H6-FLAG) protein. After extensive washing in a buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 and 500 mm NaCl, the beads were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG (top). The L, R1 or R2 domain or the full-length parkin (P), but not the U, I or GST alone (−), pulled down HDAC6. Expression levels of GST or GST-parkin constructs were shown in a separate GST blot in the bottom panel. F, Direct binding between interaction domains of HDAC6 and parkin in vitro. Purified GST (−) or GST-parkin constructs (L, R1, R2 or P) were immobilized on glutathione beads, which were incubated with purified DD1 or DD2 domain of HDAC6 (His-DD1-FLAG or His-DD2-FLAG). The beads were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG. The L or R1 domain of parkin pulled down DD1 domain of HDAC6 (top panel), while the R2 domain of parkin pulled down DD2 domain of HDAC6 (middle). GST blot of the inputs showed expression level of the GST constructs (bottom). All experiments were repeated at least three times.