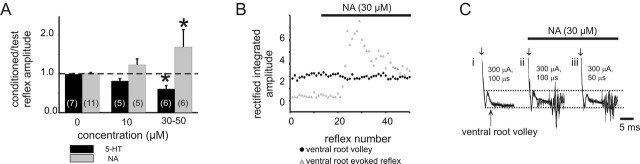
Figure 4.
NA unmasks recurrent excitatory actions. A, In experiments without detectable recurrent excitation, either 5-HT or NA was then applied at 10 or 30–50 μm. Bars represent the mean response between animals (sample size shown bracketed in histogram), and results obtained for each animal were the average of 25 reflex pairs per condition. Note that NA unmasked recurrent excitatory and 5-HT unmasked recurrent inhibitory actions in a concentration-dependent manner (∗p < 0.05). B, Comparison of amplitude of rectified/integrated ventral root volley (a measure of direct motor axon recruitment) to that of an evoked reflex. Note that the NA-evoked unmasking of the VRER occurs in the absence of changes motor axon recruitment, demonstrating that the induced recurrent excitation occurs by modulatory actions in spinal cord. C, Raw superimposed traces of evoked events at L5 after stimulation of the same root at intensities shown. i, Under control conditions, no reflex is evoked but the compound action potential representing direct motor axon recruitment is identified as an incoming ventral root volley (arrow). Note that, compared with control conditions (i), NA allows expression of an evoked reflex (ii) that persists even when the stimulation duration has been lowered (iii). Horizontal dashed lines demarcate the amplitude of the ventral root volley in control conditions to facilitate comparison between conditions.