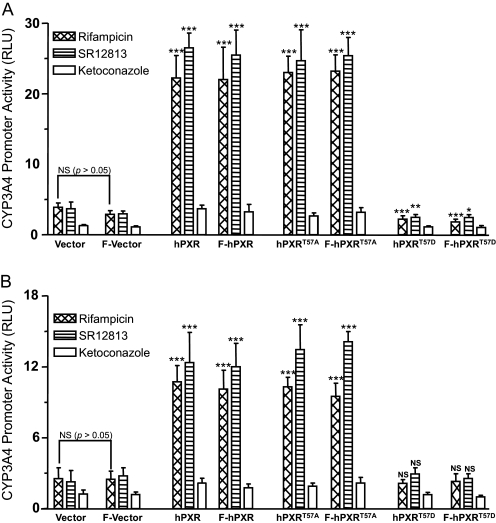
Fig. 2.
Phosphomimetic mutation at Thr57 abolishes hPXR transactivation activity. HepG2 (A) and COS7 (B) cells were cotransfected with either pcDNA3 or hPXR using CYP3A4-luc. F denotes for FLAG-tag. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, the cells were treated with vehicle DMSO (0.1%) or 10 μM compounds: rifampicin, SR12813, and ketoconazole. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h after compound treatments. CYP3A4 promoter activity induced by hPXR after treatment with the compounds was shown as RLUs. RLUs were determined by normalizing the luminescence observed in the presence of one of the compounds with the luminescence observed in the presence of DMSO. Data are shown as mean values from six independent experiments with bars indicating the S.D. The Student's t test was used to determine statistical significance of unpaired samples by comparing the RLU obtained from the samples transfected with wild-type or mutant hPXR with the samples transfected with the vector. Likewise, statistical significance was determined from the samples transfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type or mutant hPXR to the samples transfected with the FLAG vector. Furthermore, statistical significance was ascertained similarly by comparing the RLU obtained from the samples transfected with FLAG-tagged plasmids with the samples transfected with corresponding untagged plasmids, and statistics were shown only for one comparison, i.e., between the vector and FLAG vector after rifampicin treatment. No statistical significance was observed between the samples transfected with the FLAG-tagged plasmids and the untagged plasmids (statistics were not shown for all the sample comparisons). Differences were considered significant for p < 0.05 (*), 0.01 (**), or 0.001 (***), and nonsignificant (N.S.) for p > 0.05.