FIGURE 4. Stages of AVD are reflected in the response of CoroNa Green-AM (Na+) and PBFI-AM (K+) to measure changes in intracellular sodium and potassium in apoptotic Jurkat cells.
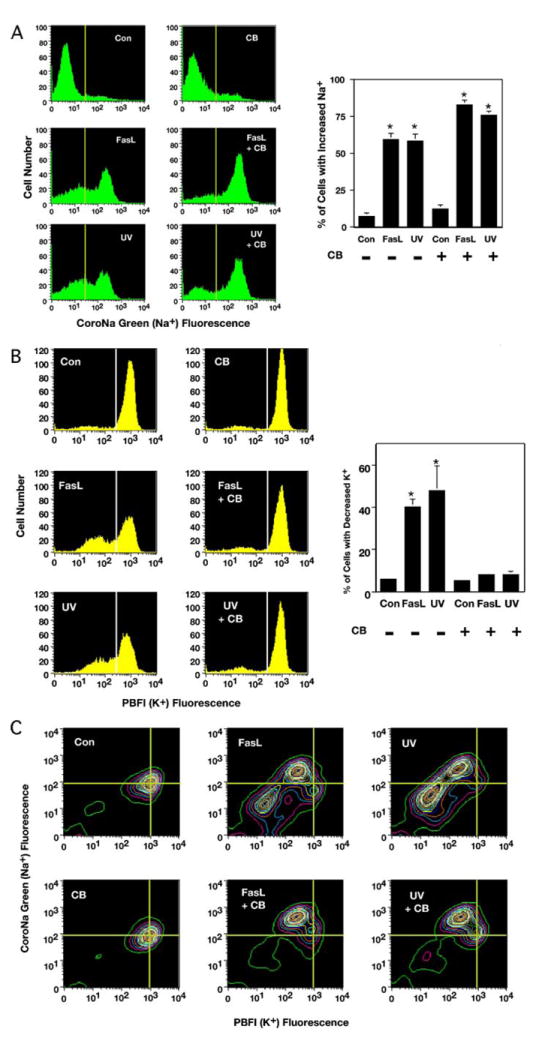
Jurkat cells treated with 50 ng/ml FasL or 60 mJ/cm2 UV in the presence or absence of 5 μm CB for 4 h were examined for changes in intracellular ions by flow cytometry. A, analysis of sodium using CoroNa Green-AM (Na+) showed an increase in intracellular sodium in apoptotic-stimulated cells regardless of the presence or absence of CB. Interestingly, this increase in intracellular sodium upon apoptotic stimulation was enhanced in the presence of CB. The histograms represent a single experiment, and the percents on the graph are the average number of three independent experiments (*, p < 0.001). B, analysis of potassium using PBFI-AM (K+) showed an efflux of intracellular potassium in the absence of CB. In contrast, cells treated with CB had a marked inhibition of intracellular potassium efflux upon induction of apoptosis (*, p < 0.001). C, simultaneous analysis of potassium and sodium using PBFI-AM (K+) and CoroNa Green-AM (Na+), respectively. Treated Jurkat cells that had an increase in intracellular sodium and a concurrent decrease in intracellular potassium regardless of the presence or absence of CB. The presence of CB prevented the continual loss of intracellular ions.
