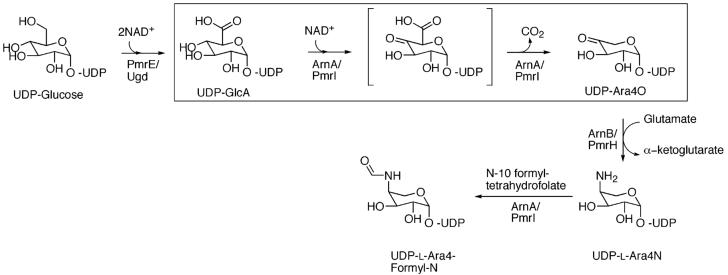
FIGURE 1.
Proposed pathway for the biosynthesis of UDP-Ara4N. The pathway starts with Ugd/PmrE oxidizing UDP-Glc to UDP-GlcA. UDP-GlcA is then oxidized at position 4 by the C-terminal domain of ArnA to yield the UDP-4-keto glucuronic acid intermediate that is then decarboxylated to UDP-4-keto arabinose by the same enzyme. UDP-Ara4O is transaminated by ArnB yielding the novel sugar-nucleotide UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-arabinose (UDP-Ara4N). The N-terminal domain of ArnA can formylate UDP-Ara4N and has been proposed to help displace the reaction catalyzed by ArnB toward UDP-Ara4N synthesis and generate a transiently formylated product (21).