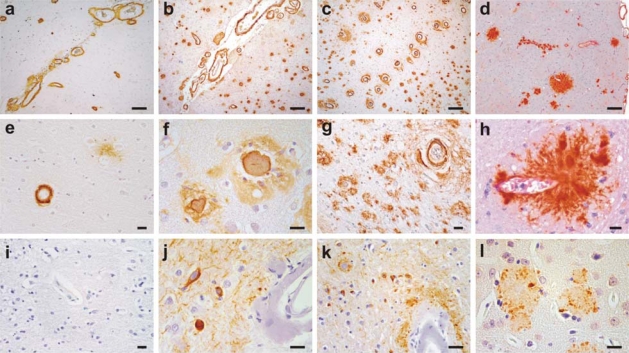
Figure 2.
Spectrum of disease from primarily hereditary amyloidosis of Dutch and Flemish type to familial forms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and to mouse models of AD.
The upper and middle panels depict Aβ staining with monoclonal antibody 4G8 in an HCHWA-D (E693Q) patient with CAA (a, e), a Flemish APP carrier with both CAA and senile plaques (b, f); a presenilin (PS)-1 L282V AD patient with senile plaques and prominent CAA (c, g), and Tg2576 mouse model with parenchymal plaques and CAA (d, h). The lower panel is phosphorylated tau staining (monoclonal antibody AT8) in temporal cortical regions of the same patients (i–k); or ubiquitin staining for Tg2576 (l). Note that HCHWA-D brains lacks dense-core senile plaque or phospho-tau pathology but do show diffuse amyloid plaques (e and i). Flemish APP and PS1 L282V carriers have phosphorylated tau immunostaining in neurofibrillary tangles, ballooned neurites and neuropil threads (j–k). Sections are immunostained with avidin-biotin complex/horseradish peroxidase system and color developed with 3’3’diaminobenzidine. Scale bars in a–d, 200 μm; and e–l, 20 μm.