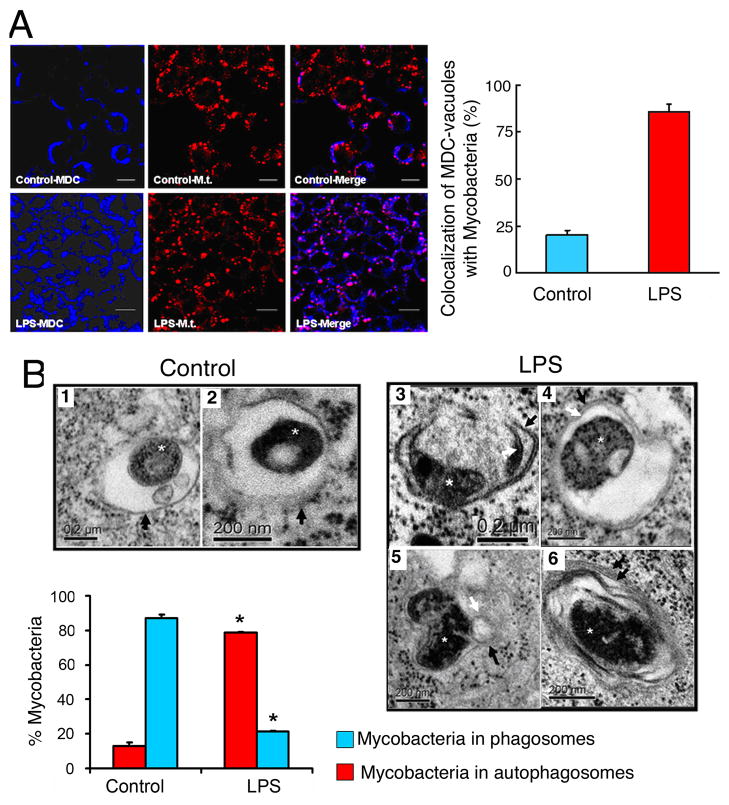
Figure 6. LPS-induced autophagy promotes the co-localization of mycobacterial phagosomes with the autophagosomes.
(A) RAW264.7 cells were infected with PKH-26-stained Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Mt, red) for 1 hr. Following phagocytosis, cells were incubated in the presence or absence of LPS for 16 hr. Cells were fixed and autophagic vacuoles were stained using Monodansylcadaverine (MDC, blue). The colocalization of Mt and the MDC-positive autophagosomes is represented in the merge panels by the pink color and quantitated in the graph in the lower panel (mean±SEM, n=2). (B) Ultrastructural analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis localization by transmission electron microscopy using RAW264.7 cells subjected to experiments as described in (A). In the absence of LPS (control), Mt bacilli were found inside typical single-membrane mycobacterial phagosome compartment, indicated by black arrows in images 1 and 2. By contrast, in the presence of LPS, Mt bacilli were found in typical double-membrane autophagosomes (images 3 and 4). Potential fusion events between mycobacterial phagosome and autophagosome were observed (image 5). Image 6 illustrates the presence of onion-like multilamellar structures containing mycobacteria. Black arrows, outer membranes; white arrows, internal membranes; double black arrows, onion-like multilamellar structures; white asterisks, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Graph represents the quantitation of 100 internalized mycobacteria per experimental condition.