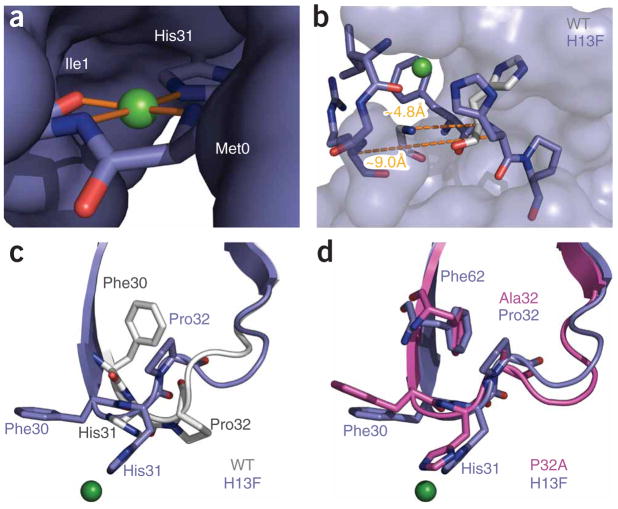
Figure 6.
Conformational effects of Cu2+ binding. (a) Copper (green sphere) shown with its coordinating ligands. The remainder of the protein is shown as solvent-accessible surface. The geometry is approximately square, with the metal cation coplanar with its ligands. Details of the binding-site geometry are summarized in Supplementary Table 1. (b) Strand A is displaced as a result of Cu2+ binding. H13Fholo (blue) is shown as sticks for residues 1–3 of strand A and 30–32 of the BC loop. The remaining residues of H13Fholo are shown as a solvent-accessible surface. His31 and the main chain of Arg3 are shown for the wild-type protein (gray). Dashed lines denote the indicated Cα-Cα separation between residues 3 and 31 of H13Fholo and the wild-type protein, respectively. (c,d) Comparison of the BC loop of H13Fholo with corresponding residues in the wild-type and P32A structures.