Figure 2. Neuroprotection by multiple receptor agonists in organotypic hippocampal slices treated acutely with NMDA.
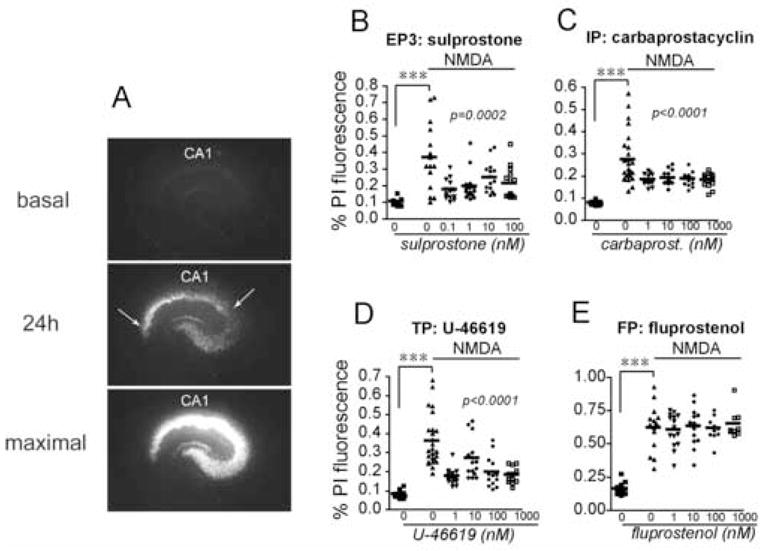
(A) Representative series of images of hippocampal slice treated with NMDA. (Top panel) Basal PI staining (time point tb; see Methods). (Middle panel) Slices were stimulated for one hour with NMDA (10 μM) and allowed to recover for 24 hours (t24h): selective PI uptake occurs in CA1 pyramidal neurons (between arrows), as well as CA2–4. (Bottom panel) Maximal pyramidal neuronal death was induced by incubating slices for an additional 24 hours with NMDA (tmax). PI fluorescence was normalized for each individual slice as follows: (t24h− tb)/(tmax− tb). (B) The PGE2 EP3 agonist sulprostone is protective at pM-nM concentrations (vehicle vs NMDA : ***p=0.0004; NMDA vs NMDA+sulprostone: ANOVA p=0.0002, post hoc p<0.001 for 0.1nM, p<0.01 for 1 nM, p<0.05 for 10 nM, and p<0.01 for 100 nM). (C) The PGI2 IP receptor agonist carbaprostacyclin protected CA1 neurons (vehicle vs NMDA : ***p=0.0001; NMDA vs NMDA+carbaprostacyclin: ANOVA p<0.0001, post hoc p<0.01 for 1nM, p<0.01 for 10 nM, p<0.01 for 100 nM, p<0.01 for 1 μM ). (D) The TXA2 TP receptor agonist U-46619 is protective (vehicle vs NMDA : ***p<0.0001; NMDA vs NMDA+ U-46619: ANOVA p<0.0001, post hoc p<0.001 for 1nM, p<0.05 for 10 nM, p<0.001 for 100 nM, and p<0.001 for 1 μM), but (E) the PGF2α FP receptor agonist fluprostenol has no effect on hippocampal CA1 neuronal survival ( ***p<0.001 control vs NMDA).
