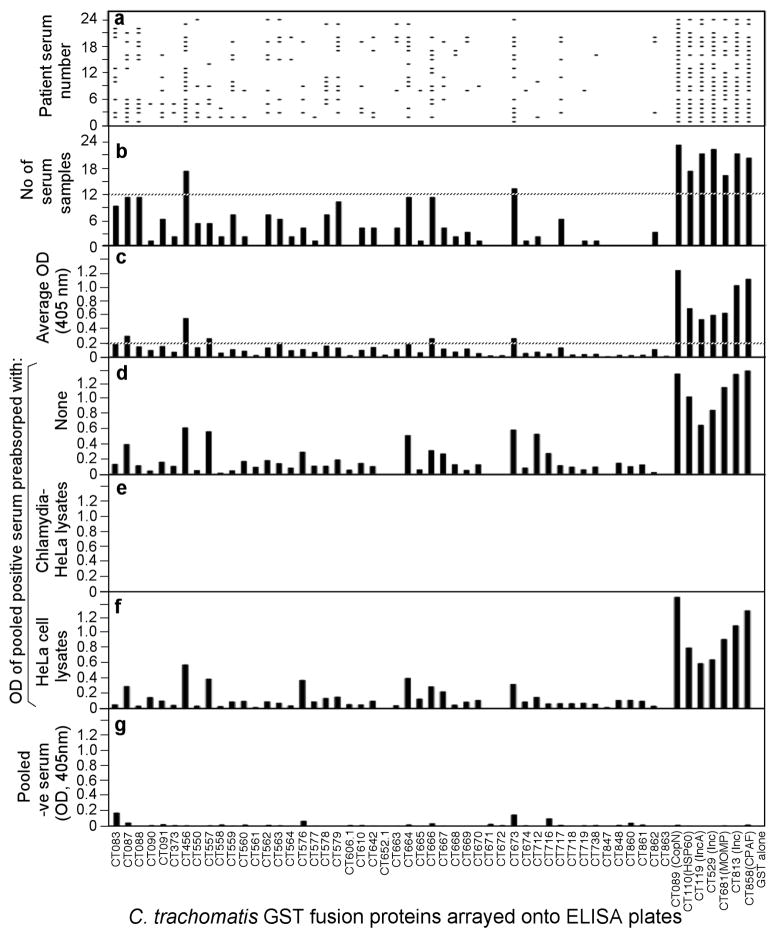
Fig. 1. Reactivity of 24 STI antisera with 55 GST-chlamydial fusion proteins.
Each of the 24 human antibodies (displayed along the Y-axis of panel a) after 1:500 dilution was reacted with each of the 55 GST fusion proteins (listed along the X-axis) immobilized onto the 96 well microplates. The human antibody binding was detected with a secondary goat anti-human IgG antibody conjugated with HRP plus a soluble substrate. The results were expressed as OD readings obtained at the wavelength of 405nm. Any given reaction with an OD reading 4 fold above the value from the control well (GST alone-coated well) was determined positive, which was represented with a horizontal bar in panel a. The total number of human serum samples that positively recognized a given fusion protein was summarized in panel b. The dotted line marked those fusion proteins recognized by 12 or more human antisera. The average OD readings calculated by dividing the total OD values by 24 were displayed in panel c. The dotted line marked those fusion proteins with an average OD of 0.2 or above. The 24 human serum samples were pooled at an equal ratio and assayed against each of the fusion proteins at a dilution of 1:200 and the OD values were displayed along the Y-axis of panel d. The pooled serum sample was also subjected to pre-absorption with either C. trachomatis serovar D-infected (panel e) or HeLa cell alone (f) lysates prior to reacting with the fusion proteins. Finally a pooled serum from 8 negative individuals failed to react with the fusion proteins (panel g).