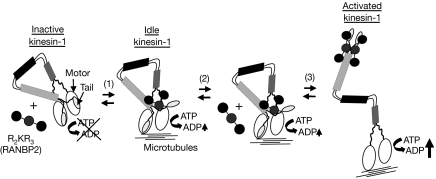
Figure 5.
Schematic modelling of the activation of kinesin-1 by the R2KR3 of RANBP2; R2KR3 is depicted as a cargo of KIF5B. Cargoless kinesin-1 is in a compact conformation with the tail folded over the motor domain causing the inhibition of the ATPase activity. At low concentrations, R2KR3 binds to one of the two bipartite binding sites in kinesin-1 and partly reverts the inhibition by the tails over its motor domain, generating an idle kinesin-1 with low ATPase activity (1). At high concentration of R2KR3 (2), the bipartite sites on both chains become occupied (3). This leads to an extended (relaxed) kinesin-1 by tight conformational coupling and boosting of the motor activity of kinesin-1 in the presence of microtubules (3). KIF5, kinesin superfamily protein 5; RANBP2, RAN-binding protein 2; R2KR3, RBD2–KBD–RBD3.