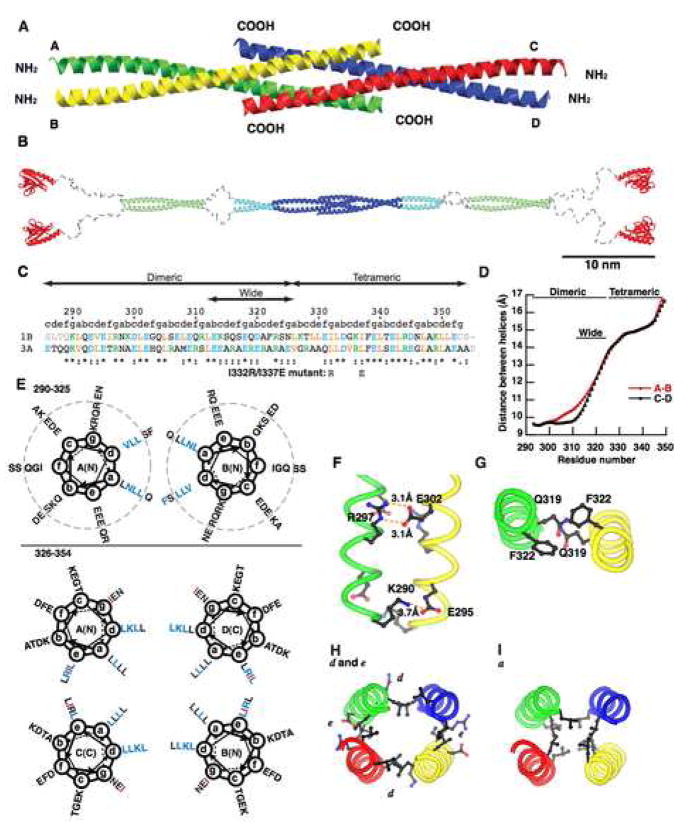
Figure 3. Crystal structure of the Homer coiled-coil region.
(A) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal half of Homer1b coiled-coil region CC2. The four strands are marked A–D.
(B) A model of the whole structure of long form of Homer. The model is constructed from the structure of the Homer1CC2 domain (blue), EVH1 domain (red) (Irie et al., 2002), and coiled-coil probability prediction and protease degradation sites (Hayashi et al., 2006). The CC1 and a part of the CC2 domain, whose atomic structures are not known, are in light green and light blue, respectively. Regions likely to be disordered are shown in grey.
(C) Primary sequence of the crystallized fragment. 1B, rat Homer1b; 3A, human Homer3a. Orange, aliphatic residues (I, L, V); blue, acidic (D, E); green, basic (K, R); grey, residues not in crystals. Mutations made in dimeric Homer1b I332R/I337E are shown below. “abcdefg” denotes positions in the heptad of coiled-coil.
(D) Distance between the A and the B strand, or the C and the D strand, are measured and plotted against the number of residues.
(E) Helical wheel representation of the dimeric (top) and tetrameric (bottom) region of Homer1b. Residues start from K290 at g position. Residues which make knobs-into-holes interactions with residues on the other strands are shown in blue. Residues changed in the dimeric mutant (I332 and I337) are shown in red. Residues outside the dotted circles are located within the wide dimeric region.
(F) Example of intermolecular salt bridges formed between residues at the e (E295 and E302) and g (K290 and R297) positions within the dimeric region.
(G) Large amino acids occupying the a and d positions in the wide dimeric region, Q319 and F322.
(H) Inter-chain interactions in the tetrameric region. Residues at d positions (L329, K336, L343, L350) form the A–D and B–C interface, and those at e positions (L330, I337, R344, L351) form the A–C and B–D interface.
(I) Hydrophobic core formed by leucines at a positions (L326, L333, L340, L347).