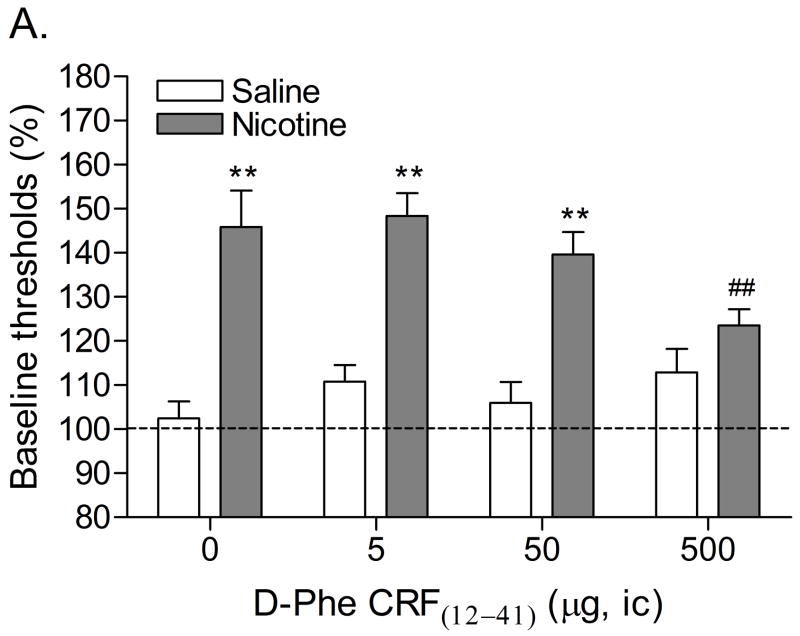
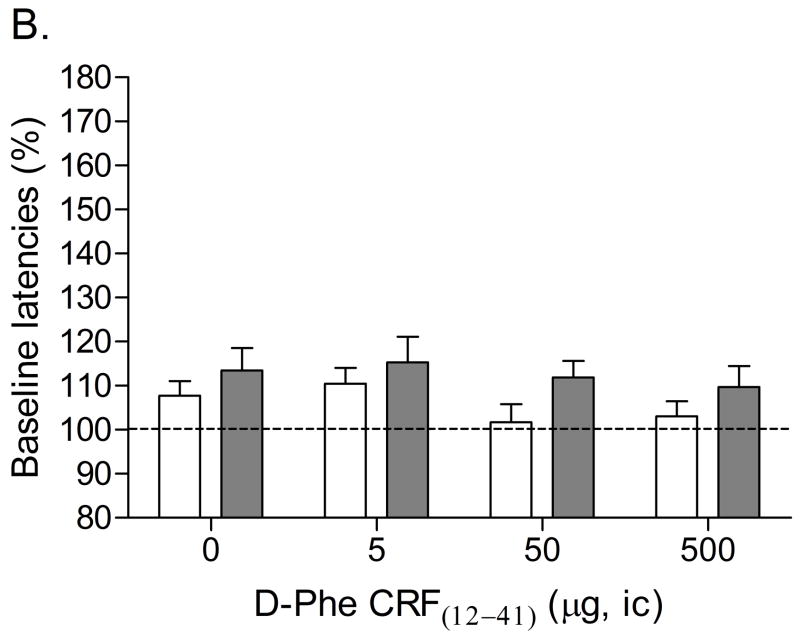
Figure 1.
Effect of D-Phe CRF(12–41) (saline, n = 8; nicotine, n = 8) administered into the CeA on the elevations in brain reward thresholds associated with mecamylamine-precipitated nicotine withdrawal (A). Effect of D-Phe CRF(12–41) on the response latencies of rats chronically treated with saline (n = 8) or nicotine (n = 8) and acutely treated with mecamylamine (B). Brain reward thresholds and response latencies are expressed as a percentage of the pre-test day values. D-Phe CRF(12–41) was administered bilaterally and the figure depicts the unilateral dose. Asterisks (** P<0.01) indicate elevations in brain reward thresholds compared to those of the corresponding saline-treated control group. Pound signs (## P<0.01) indicate lower brain reward thresholds compared to those of rats chronically treated with nicotine and acutely treated with mecamylamine and vehicle (0 μg of D-Phe CRF(12–41)). Abbreviation: ic, intracranial.