Figure 8.
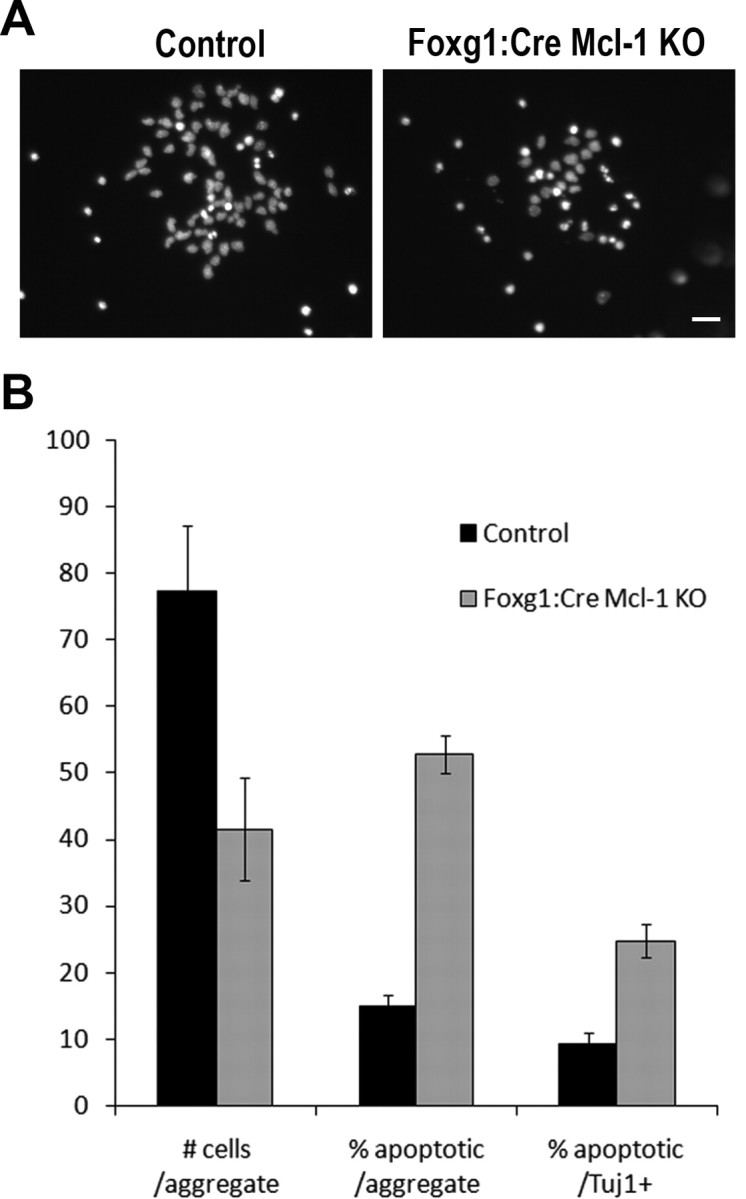
Mcl-1 deficient cortical progenitor cell death is cell autonomous. Cortical progenitor cell aggregates were plated at similar plating densities and allowed to differentiate in culture while survival was monitored. Cell survival was assessed with Hoechst nuclear staining to distinguish both viable (diffuse Hoechst nuclear staining) and apoptotic (condensed nuclei) cells. A, Representative photomicrographs of Hoechst-stained control and Mcl-1 deficient E12.5 cortical precursor cultures after 3 DIV. B, Counts were performed to quantify the total number of cells (viable and apoptotic) per aggregate (represented as mean number of cells/aggregate) and the number of apoptotic cells per aggregate (represented as percentage of apoptotic). Tuj1 immunostaining was performed to determine whether cortical precursors were capable of committing to a neuronal phenotype before dying. The number of apoptotic cells that were also Tuj1 positive (Tuj1+) were counted and compared with the number of Tuj1+ cells per aggregate (represented as percentage of apoptotic/Tuj1+). Results are summarized from six different platings of each genotype derived from two independent animals. Scale bar, 25 μm.
