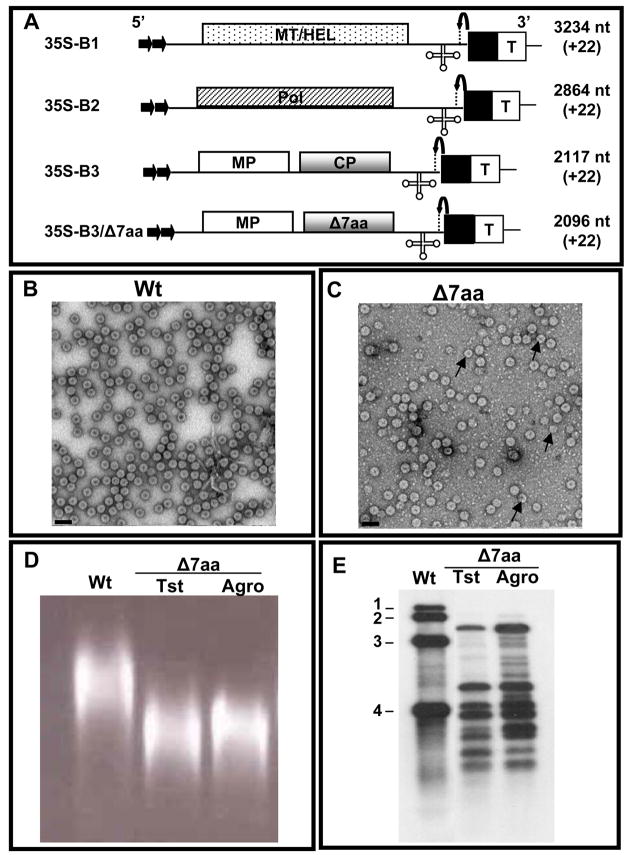
Figure 4.
Biological activity of Δ7aa induced by agroinfiltration. (A) Characteristics of T-DNA plasmids of wt BMV genomic RNAs and B3/Δ7aa used for Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression in plants. The 35S-B1, 35S-B2 and 35S-B3 constructs contain full-length cDNA copies of BMV genomic RNAs 1 (B1), 2 (B2) and 3 (B3) respectively (Annamalai and Rao, 2005). Filled arrows at the 5′ end represent the location of double 35S promoter (35S) whereas filled square and T respectively denote ribozyme sequence cassette derived from satellite tobacco ring spot virus and the 35S-polyadenylation terminator signals. Bent arrow at the 3′ end represents ribozyme cleavage site. The lengths of wt BMV RNAs and the number of non viral nucleotides left after self-cleavage by ribozyme (shown in bracket) are indicated. (B and C) Electron micrographic images of partially purified virions of wt (B) and Δ7aa (C) from agroinfiltrated N. benthamiana plants. In panel C, the smaller size particles are indicated by the arrow head. Bar = 50 nm. (D) Virion mobility profiles. Partially purified virions of Δ7aa from plant infected either with in vitro transcripts (Tst) or by agroinfiltration (agro) were subjected agrose gel electrophoresis as described under Fig. 1 legend. Agroinfiltration derived wt virion preparation was used as a control. (E) Northern blot analysis. RNA isolated from virions of Δ7aa purified from plants infected either with in vitro transcripts (Tst) or by agroinfiltration (agro) was subjected to Northern blot hybridization with a riboprobe complementary to the 3′ TLS as described under Fig. 2 legend. Virion RNA of wt BMV was used as a marker.