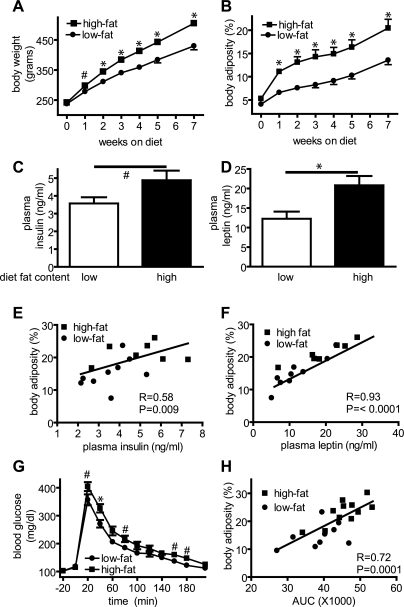
Fig. 1.
Effect of high-fat feeding on body weight and composition, plasma hormone levels, and glucose tolerance. Effects of consuming either a low- or high-fat diet on body weight (A) and body adiposity (B) and on plasma insulin (C) and leptin (D) levels. Differences in plasma concentrations of insulin (E) and leptin (F) across groups were significantly correlated with changes of body adiposity (r = 0.58 and r = 0.93, respectively; P < 0.01 for each), as were differences in the blood glucose concentration measured during an intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test and area under the curve (AUC) of glucose excursion was significantly correlated with adiposity (r = 0.72; P = 0.0001; G and H). #P < 0.05; *P < 0.01.