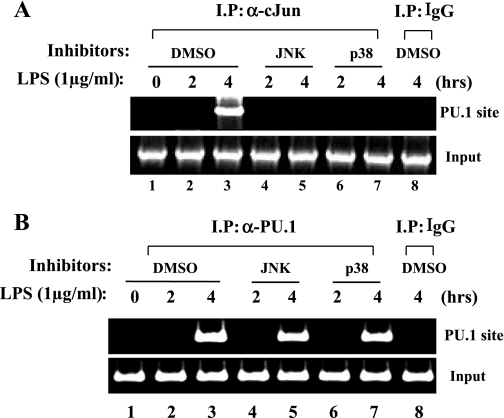
Fig. 5.
PU.1 binding to the cognate site occurs without cJun. A: to examine whether cJun binding to the PU.1 site is affected by either JNK or p38 kinase, we performed a ChIP assay. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with DMSO (lanes 1–3) or 10 μM JNK inhibitor (lanes 4 and 5) or p38 kinase inhibitor (lanes 6 and 7) 1 h before LPS treatment. DNA bound to cJun was precipitated by the α-cJun antibody and amplified by PCR with the set of primers flanking the PU.1 site (top). To exclude nonspecific immunoprecipitation, we added an isotypic IgG to the nuclear fraction of the cells treated with LPS for 4 h (lane 8). Genomic DNA (100 ng) was amplified by PCR as input controls (bottom). B: to measure the possible effect of JNK or p38 kinase on binding of PU.1 to the PU.1 binding site, we performed a ChIP assay with the α-PU.1 antibody (lanes 1–7) or an isotypic IgG (lane 8). Precipitated DNA was amplified by PCR with the set of primers flanking the PU.1 binding site (top). Similarly, genomic DNA was amplified (bottom).