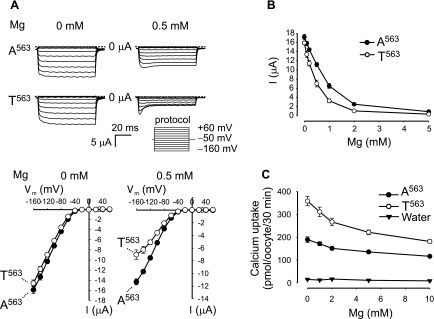
Fig. 5.
Decreased Na+ current of T563 variant was due to increased sensitivity to extracellular Mg2+. A: representative Na+ current traces of A563 and T563 variants in the presence of 0 and 0.5 mM extracellular Mg2+ are shown in top. The I-V curves of Na+ current for A563 and T563 were parallel in the absence of extracellular Mg2+ and departed in the presence of 0.5 mM extracellular Mg2+ (bottom). B: Na+ current of the T563 variant was more sensitive to extracellular Mg2+ concentration than that of the A563 variant. Currents at −160 mV from two independent experiments of 18 oocytes/group are expressed as means ± SE. Flufenamic acid at 200 μM was included in the solutions to block the Ca2+-inactivated Cl− current induced by the removal of both Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the extracellular solution. C: effect of extracellular Mg2+ on 45Ca2+ uptake mediated by oocytes expressing A563, T563, or by water-injected control oocytes (water). Mg2+ (10 mM) in the extracellular medium led to a stronger reduction in Ca2+ uptake in oocytes expressing T563 than those expressing A563 (49.4 ± 2.2 vs. 38.5 ± 2.5%). Data from 3 independent experiments are expressed as means ± SE.