Fig. 6.
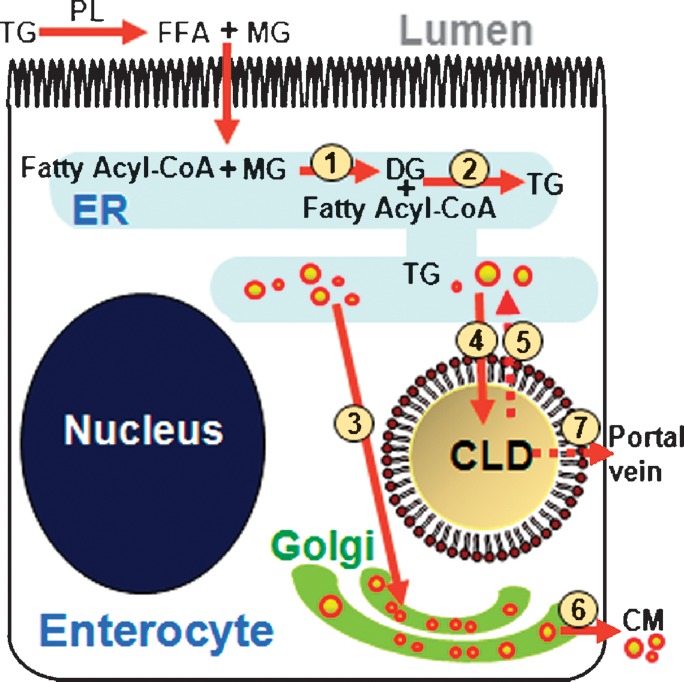
Model of the DFA process based on the finding of TG storage in CLDs within enterocytes. Dietary TG is hydrolyzed in the small intestine lumen by pancreatic lipase to FFA and MG. These products are taken up by the enterocyte where they are rapidly resynthesized in ER (steps 1 and 2) to form TG. Within the ER, the TG is packaged in the core of CMs where it is secreted via the Golgi complex into lymphatics (steps 3 and 6). Alternatively, TG synthesized in the ER may be stored in CLDs (step 4). TG stored in CLDs may be hydrolyzed by a lipase, such as pancreatic TG lipase or TG hydrolase. The hydrolyzed products of TG from CLDs may be transported back to the ER (step 5) and reenter the secretory pathway (steps 3 and 6) or excreted via the portal vein (step 7). Alternatively, hydrolyzed products may be catabolized within the enterocyte or used for other complex lipid synthesis, such as cholesterol esters or phospholipids (data not shown). DG, diacylglycerol; PL, pancreatic lipase.
