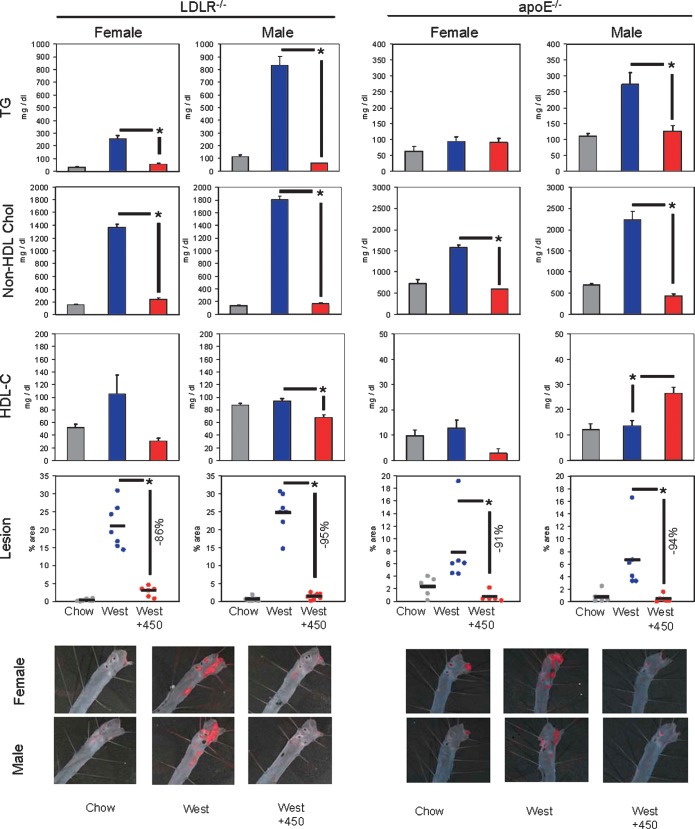
Fig. 2.
WAY-362450 inhibition of dyslipidemia and aortic atherosclerosis. Female or male LDLR−/− or apoE−/− mice 8–10 weeks of age were fed a chow diet, a Western diet containing 0.2% cholesterol, or the Western diet supplemented to deliver ∼30 mg/kg body weight of WAY-362450. LDLR−/− mice were fed the diets for 12 weeks; apoE−/− mice were fed the diets for 6 weeks. At the completion of the study, mice were euthanized, with aortas harvested for lesion analysis, liver and ileums frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA analysis, and plasma collected by retro-orbital puncture for lipid analysis. Plasma total TG and total cholesterol contents were quantified using a Roche 912 Clinical Chemistry analyzer. Non-HDL (summed VLDL + LDL cholesterol) and HDL cholesterol levels were determined by fast performance liquid chromatography as previously described (17). Aortas were stained by oil red O, and the percentage of area covered was determined. * P < 0.01 for WAY-362450 treatment versus Western diet alone; n = 5–7 mice per group.