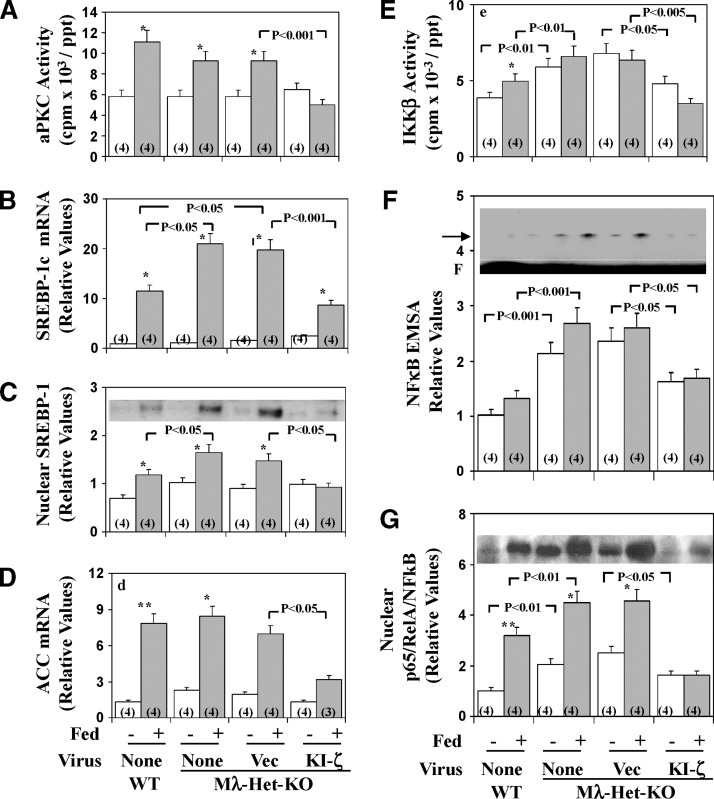
Fig. 8.
Effects of adenovirally mediated expression of kinase-inactive (KI) PKC-ζ on basal and feeding-induced hepatic aPKC activity (A), SREBP-1c mRNA (B), active nuclear SREBP-1 fragment (C), ACC mRNA (D); IKKβ activity (E), NFκB electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) activity (F), and nuclear p65/RelA/NFκB subunit levels (G) in heterozygous muscle-specific PKC-λ knockout (Mλ-Het-KO) mice. Mλ-Het-KO mice were either not injected (None) or injected IV with adenovirus vector (Vec) or adenovirus encoding KI-PKC-ζ (KI-ζ). Four days later (to allow time for expression), mice were fasted overnight (clear bars) or maintained on their usual low-fat, normal-chow diet (shaded bars). For comparisons in assays, wild-type (WT) littermates were similarly fasted or maintained on low-fat, normal-chow diet. Mice were killed on the fifth day after virus treatment, and muscles, livers, and sera were harvested. Values are mean ± SEM of (N) determinations. Arrow in panel F indicates electrophoretic mobility of the NFκB-DNA complex as determined with the kit standard; F indicates the electrophoretic front. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 (*), P < 0.01 (**), and P < 0.001 (***) for feeding-stimulated values versus adjacent basal fasting values. P values depict comparisons of indicated groups. All P values were determined by ANOVA. Representative immunoblots of the active nuclear SREBP-1 fragment and the nuclear p65/RelA/NFκB subunit (C and G insets, respectively). Representative autoradiogram of an NFκB EMSA gel-shift assay (F inset).